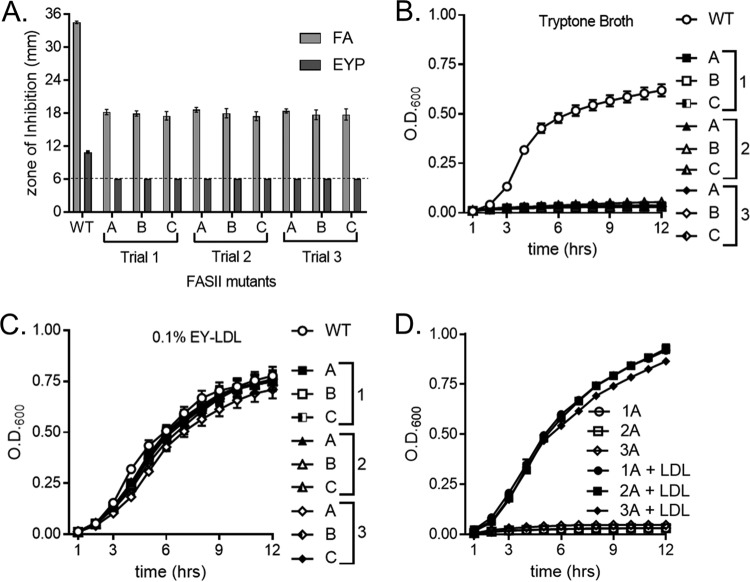
FIG 8.
LDL supplements the growth of triclosan-resistant, fatty acid auxotrophs. (A) Triclosan-resistant fatty acid auxotrophs were plated as a lawn on TSA with the following supplement: fatty acid mixture or 1% EYP. A triclosan-impregnated disk was placed on top of the agar. The dashed line denotes the limit of detection of 6 mm. The mean diameter of the zone of inhibition from three independent experiments is shown. All error bars represent the standard error of the mean. (B) The growth of the triclosan-resistant fatty acid auxotrophs in 1% tryptone broth was monitored over time by measurement of the OD. (C) The growth of the triclosan-resistant fatty acid auxotrophs in 1% tryptone broth with 0.1% purified egg yolk LDL (EY-LDL) was monitored over time by measurement of the OD. Squares represent mutants isolated in trial 1, triangles denote mutants isolated in trial 2, and diamonds depict mutants isolated in trial 3. The mean results from four independent experiments are shown. All error bars represent the standard error of the mean. (D) The growth of a representative triclosan-resistant fatty acid auxotroph from each trial was monitored over time by measurement of the OD600. Cells were grown in 1% tryptone broth under the following conditions: untreated or supplementation with 0.34 μg/μl purified human LDL. The mean results from three independent experiments are shown. All error bars represent the standard error of the mean.