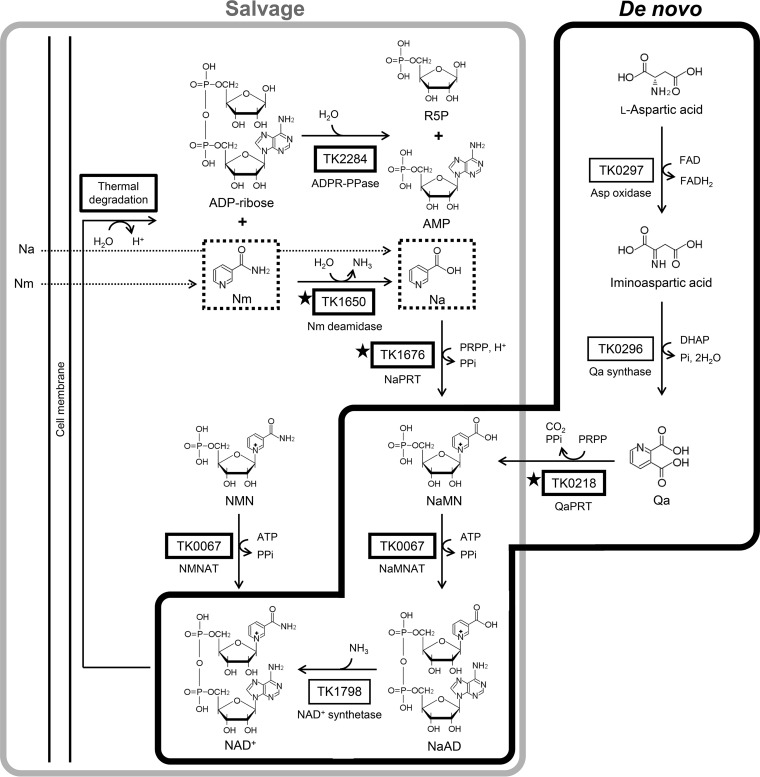
FIG 5.
Predicted de novo and salvage pathways for NAD+ biosynthesis in T. kodakarensis. Thick-lined boxes represent proteins or reactions that have been characterized in T. kodakarensis. Those with stars indicate proteins examined in this study. Dotted boxes show compounds that can be taken up by the cell, based on the results of this study. Other reactions in this figure are based on studies on homologous proteins from other archaea, such as TK0297 homologs from Pyrococcus horikoshii (40), from Sulfolobus tokodaii (41), and from Thermococcus litoralis (42), TK0296 homologs from P. horikoshii (43) and from Pyrococcus furiosus (44), and a TK1798 homolog from Methanocaldococcus jannaschii (38). ADPR-PPase, ADP-ribose pyrophosphatase; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone phosphate; FAD, flavin adenine dinucleotide; NaAD, nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide; Na, nicotinic acid; NaPRT, nicotinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase; NaMNAT, nicotinic acid mononucleotide adenylyltransferase; Nm, nicotinamide; NmPRT, nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase; NMNAT, nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase; PRPP, phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate; Qa, quinolinic acid; QaPRT, quinolinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase; R5P, ribose 5-phosphate.