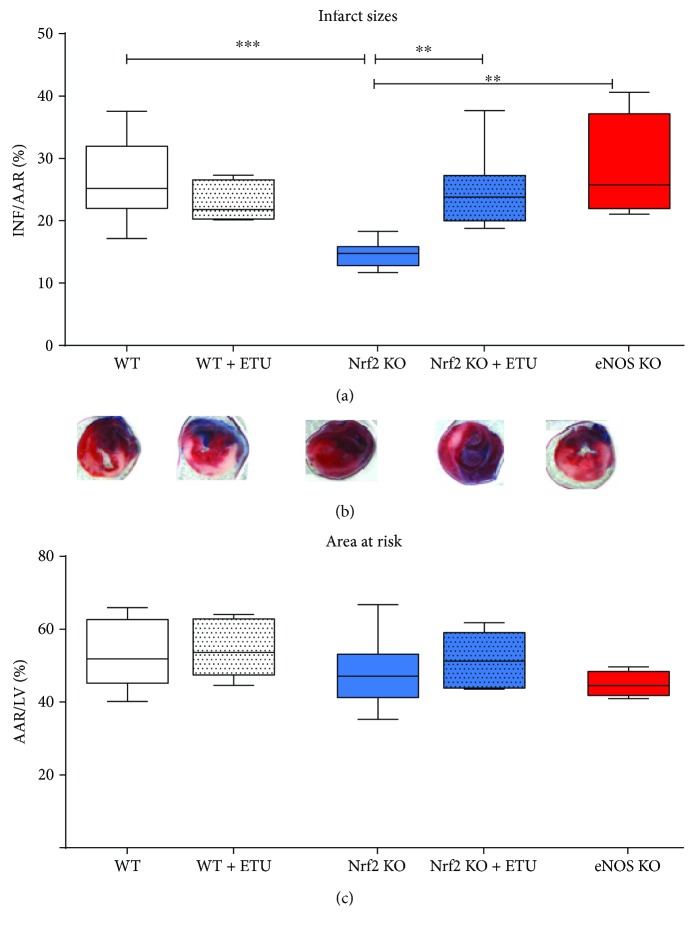
Figure 2.
NOS-dependent decrease of infarct size in Nrf2 KO mice. (a) Infarct sizes (INF) per area at risk (AAR). Nrf2 KO mice showed a significant decrease in infarct sizes as compared to WT mice. Application of the NOS inhibitor ethylthiourea (ETU) in WT mice did not affect infarct size, whereas ETU application in Nrf2 KO mice increased I/R injury demonstrating the cardioprotective role of NOS activity despite a compromised antioxidative reserve capacity in Nrf2 KO mice. eNOS KO mice showed no differences in I/R injury as compared to WT and WT + ETU mice. WT mice: n = 9, Nrf2 KO mice: n = 8, eNOS KO mice: n = 4‐5; Browne-Forsythe test p = 0.27, means ± quartiles, one-way ANOVA ∗∗ p < 0.01, ∗∗∗ p < 0.001. (b) Representative TTC stained heart sections of each strain 24 h after AMI. (c) Comparable values of area at risk/left ventricle demonstrate the reproducibility of the I/R surgery (Browne-Forsythe test p = 0.24, means ± quartiles, one-way ANOVA, ns).