Figure 2.
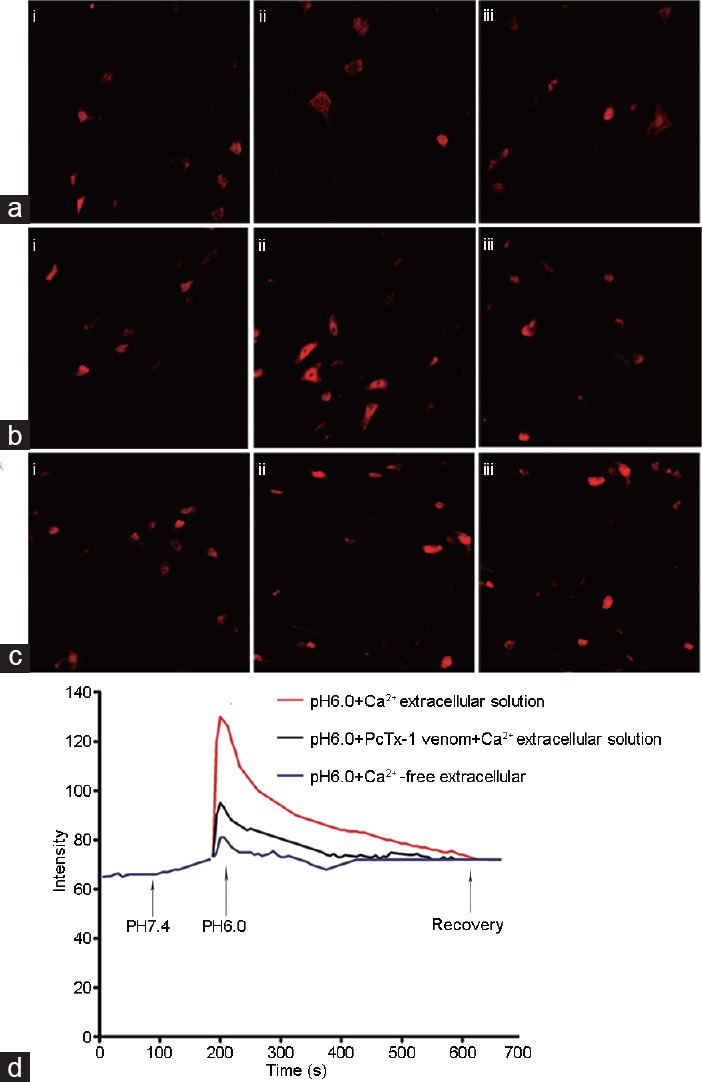
Effect of ASIC1a on [Ca2+]i in acid-treated dorsal horn neurons of rat spinal cord. (a) [Ca2+]i intensity in the acid-treated dorsal horn neurons exposed to Ca2+-free extracellular solution. (b) [Ca2+]i intensity in the acid-treated dorsal horn neurons exposed to extracellular Ca2+-containing solution. (c) [Ca2+]i intensity in the acid-treated dorsal horn neurons in the presence of PcTx-1. (d) Summary of data demonstrating changes in [Ca2+]i intensity in the dorsal horn neurons of rat spinal cord. (i) before exposure to acid solution; (ii) when the pH was decreased to 5.9; (iii) a few minutes after exposure to the acid solution (n = 7 per treatment). ASICs: acid-sensing ion channels.
