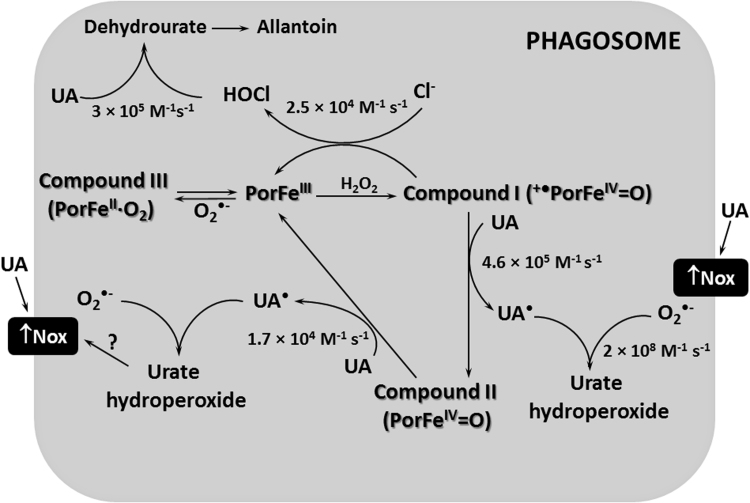
Fig. 7.
Uric acid decreases HOCl levels in the phagosome. Uric acid (UA) competes with chloride by the myeloperoxidase-Compound I (+•PorFeIV=O). Uric acid also donates one electron to myeloperoxidase-Compound II (PorFeIV=O), completing the peroxidase cycle of the enzyme (PorFeIII). This competition and the direct reaction of uric acid with hypochlorous acid (HOCl) are likely the main mechanisms responsible by the decrease in HOCl levels. Uric acid has been described by indirectly activate NADPH oxidase (Nox) and increase superoxide (O2•-) production. Superoxide can react with uric acid free radical (UA•) to form urate hydroperoxide. Superoxide is also a substrate for myeloperoxidase to generate Compound III (PorFeIV∙O2) and yet can dismutate to generate the hydrogen peroxide substrate. The rate constants for some reactions are presented.