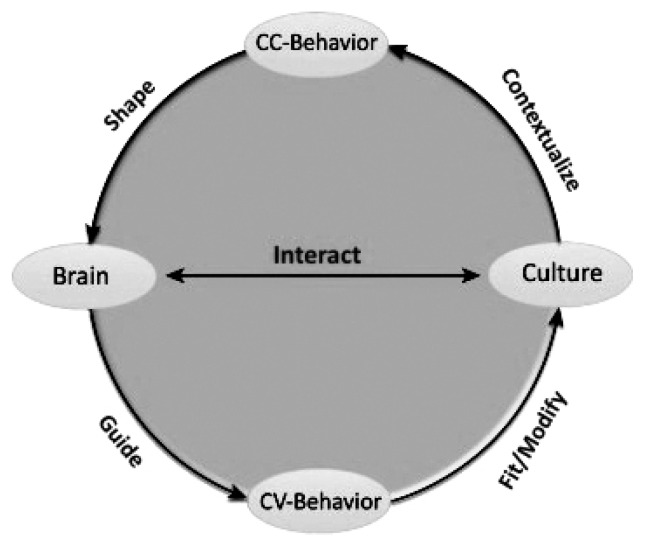
Fig. 1.
Illustration of the culture–behavior–brain (CBB) loop model of human development. Cultural environments contextualize human behaviors. Learning novel cultural beliefs and the practice of different behavioral scripts in turn modify the functional organization of the brain. The modified brain then guides individual behavior to voluntarily fit into a cultural context and meanwhile to modify current cultural environments. Direct interactions also occur between culture and brain without overt behavior.
CC-Behavior, culturally contextualized behavior; CV-Behavior, culturally voluntary behavior.
Reused from the article of Han and Ma (Trends Cogn Sci 2015;19: 666–676)58) with original copyright holder’s permission.