Figure 5. Phenotypic and functional characterization of HLA-A24 multipeptide-specific CTL generated with a cocktail of XBP1 UN185-193 (I S P W I L A V L), XBP1 SP223-231 (V Y P E G P S S L), CD138265-273 (I F A V C L V G F) and CS1240-248 (L F V L G L F L W) peptides.
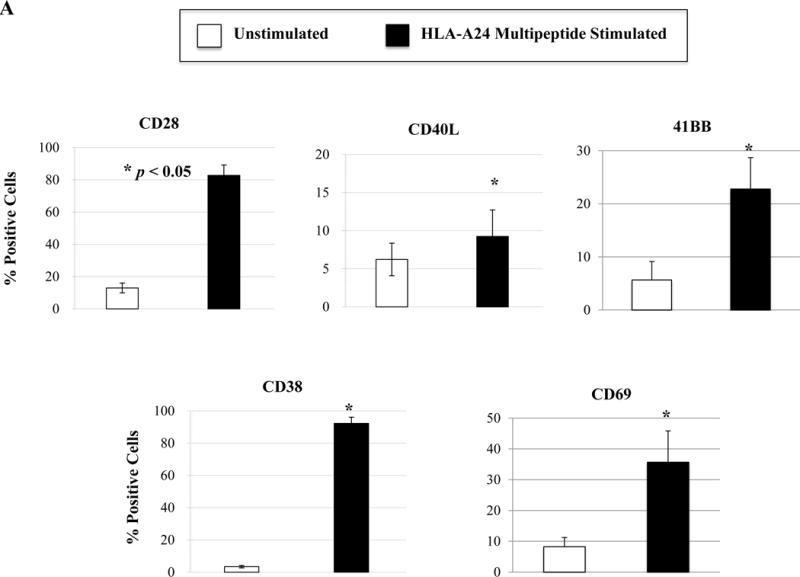
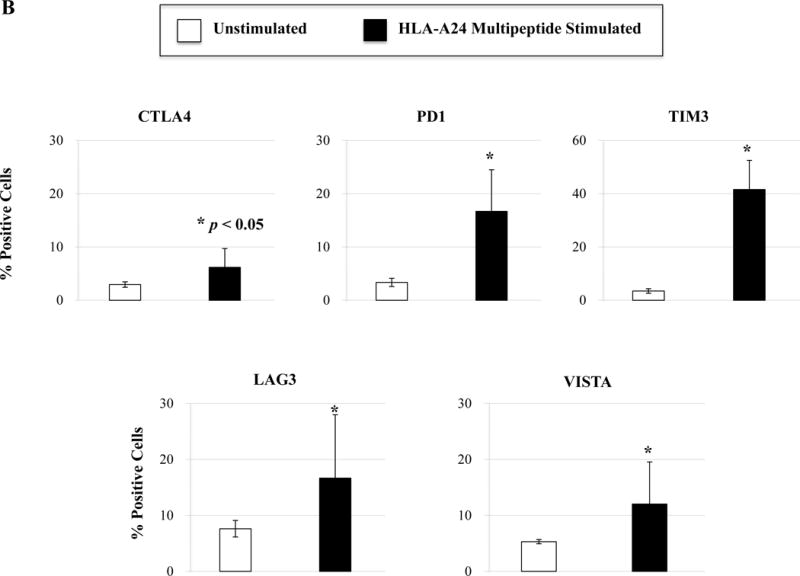
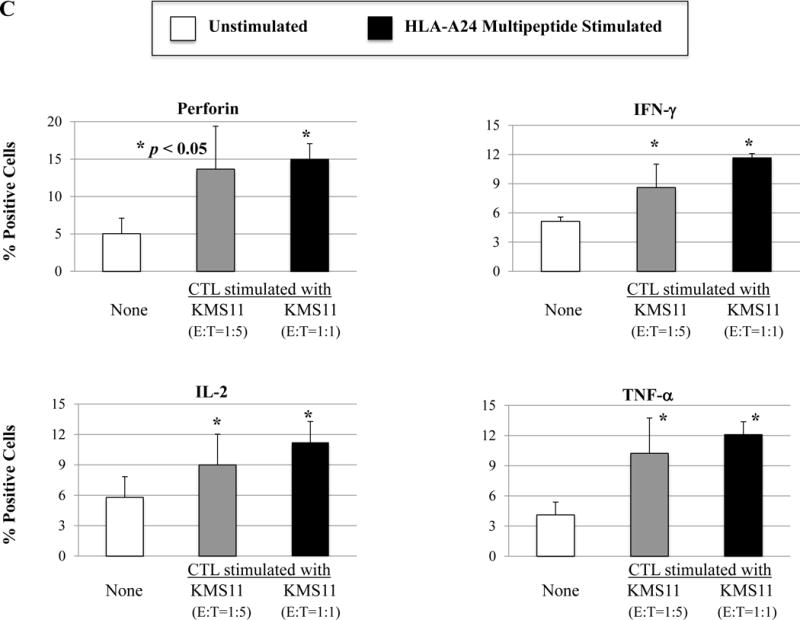
Phenotypic and immune functional characterization of multipeptide-specific CTL was performed one week after the fourth stimulation with a cocktail of the four HLA-A24 peptides (XBP1 UN185-193, XBP1 SP223-231, CD138265-273, CS1240-248). The multipeptide-specific CTL displayed increased CD3+CD8+ T cells expressing co-stimulatory molecules (CD28, CD40L, 41BB) and activation molecules (CD38, CD69) (Figure 5A) (n=3, mean ± SE). The CTL also expressed immune checkpoint antigens including CTLA4, PD1, TIM3, LAG3 and VISTA (Figure 5B) (n=3, mean ± SE). In addition, the multipeptide-specific CTL demonstrated functional anti-tumor activities including perforin and cytokines (IFN-γ, IL-2, TNF-α) production in response to HLA-A24+ KMS11 myeloma cells at both Effector:Target ratios tested (1:5, 1:1) (Figure 5C) (Average ± SE; N=5).
