Figure 6. Differentiation and development of memory CD3+CD8+ subsets upon repeated stimulation with a cocktail of XBP1 UN185-193 (I S P W I L A V L), XBP1 SP223-231 (V Y P E G P S S L), CD138265-273 (I F A V C L V G F) and CS1240-248 (L F V L G L F L W) peptides.
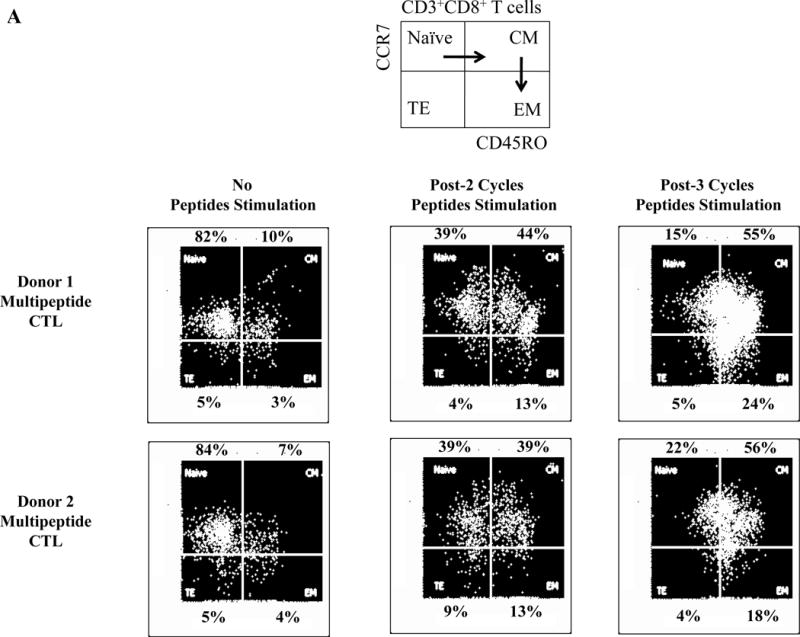
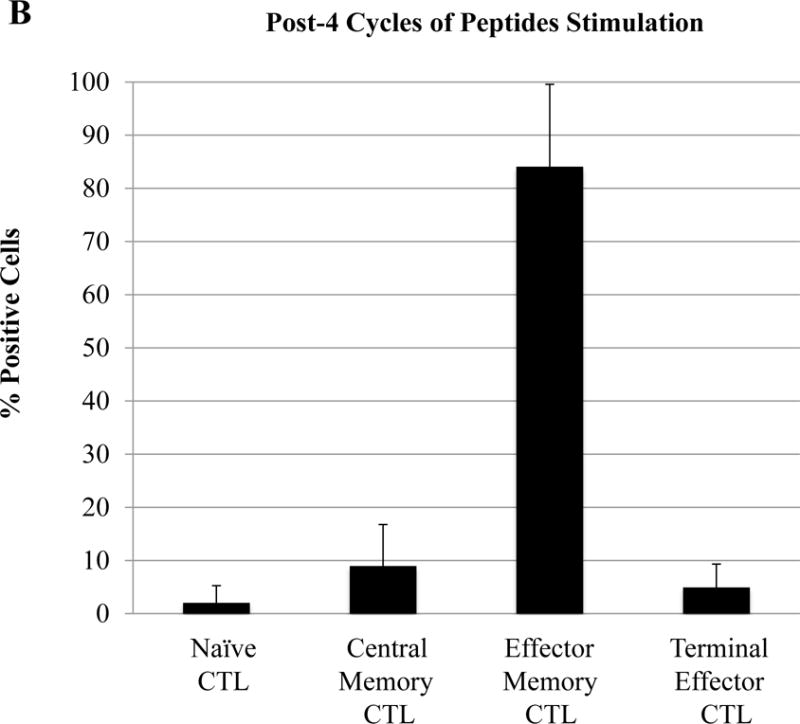
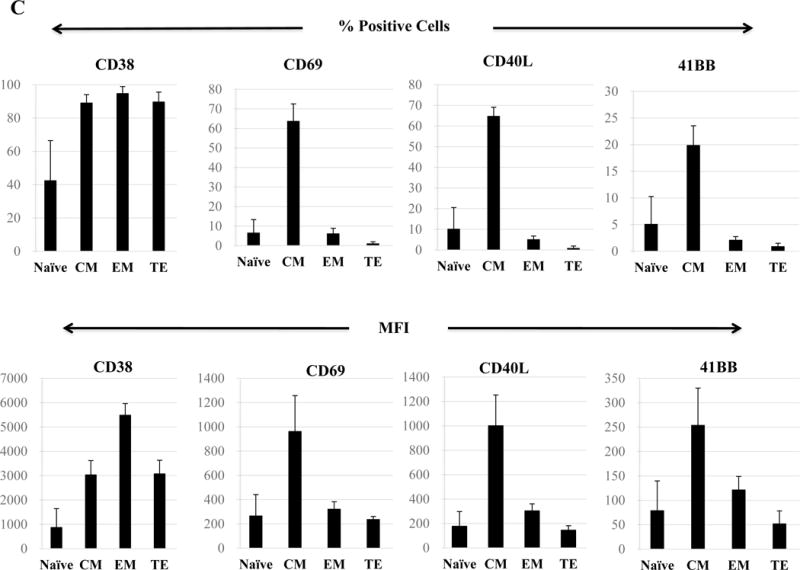
The Naïve:Memory CD3+CD8+ CTL subsets were characterized following each round of stimulation with HLA-A24 multipeptide cocktail. Repeated multipeptide stimulation of CD3+ T cells from HLA-A24+ donors (N=5) induced phenotypic changes from naïve (CD45RO−CCR7+) CD3+CD8+ T cells into central memory (CD45RO+ CCR7+) CD3+CD8+ T cells after 2 cycles of peptides stimulation and then into effector memory (CD45RO+ CCR7−) CD3+CD8+ T cells after 3 cycles of stimulation (Figure 6A), and then into effector memory (CD45RO+ CCR7−) CD3+CD8+ T cells after 4 cycles of stimulation (Figure 6B). Within the multipeptide-specific CTL population, the central memory subset expressed the highest levels of critical activation and co-stimulatory T cell markers (CD38, CD69, CD40L, 41BB; Figure 6C)
