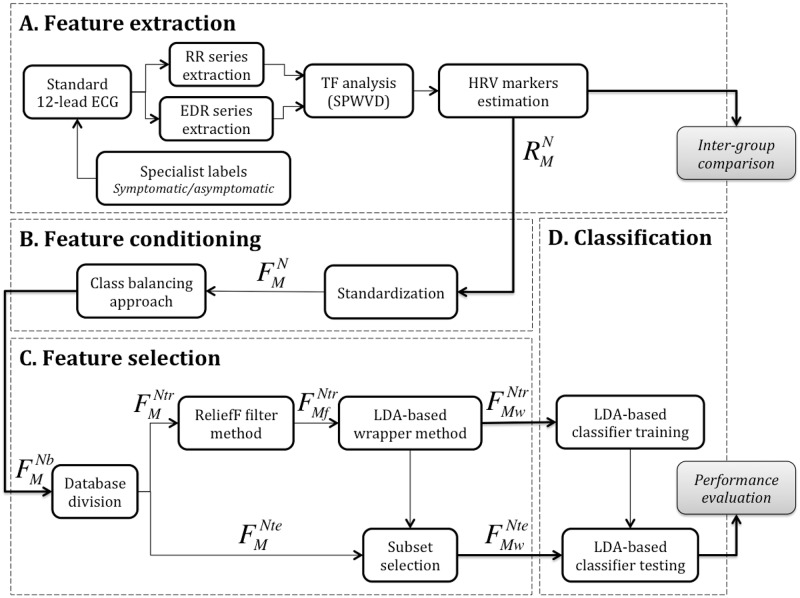
Fig 1. General diagram of the proposed classification methodology.
Data processing is composed of four major steps. A) Feature extraction is focused on the estimation of a matrix of time-frequency HRV markers (, with N = 105 patients and M = 60 different HRV features), using a time-varying frequency band that depends on the estimated instantaneous respiratory rate. B) Feature conditioning consists on standardizing and balancing , leading to matrices and , respectively, where Nb refers to the 160 observations after class balancing (79 symptomatic and 81 asymptomatic samples). C) Feature selection, which starts by randomly defining patient subsets for training, (Ntr, 75% of patients, 59 symptomatic and 60 asymptomatic) and testing (Nte, the rest of patients, 20 symptomatic and 21 asymptomatic), followed by the estimation of a minimal feature dimension Mw < M, that maximizes classification performance, using filtering and wrapper methods. D) The final step is dedicated to classification and performance evaluation.