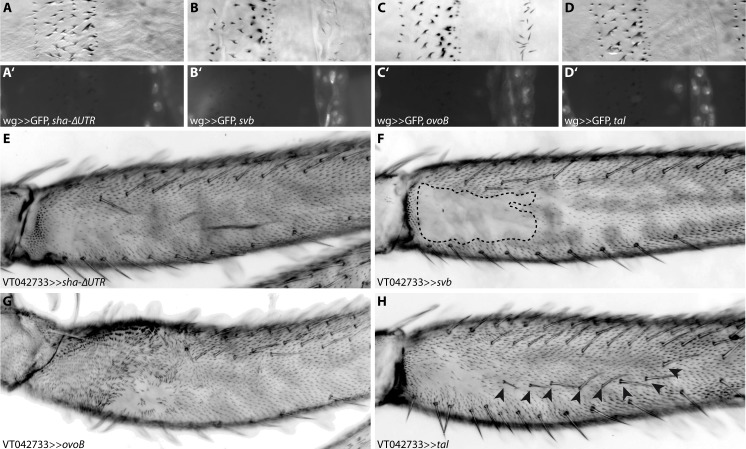
Fig 4. Ectopic trichome formation on naked cuticle.
Driving sha-ΔUTR (A) under control of wg-GAL4 does not lead to ectopic trichome formation on otherwise naked larval cuticle. Driving svb (B) or its constitutively active variant ovoB (C) is sufficient to activate trichome development, but expressing only the Svb activator tal (D) is not [32,38]. GFP was co-expressed in each case to indicate the wingless (wg) expression domain (A’-D’). Ectopic activation of sha-ΔUTR in the proximal femur (E) is able to induce trichome formation, but ectopic svb (F) is not. Driving either ovoB (G) or the activator tal (H) leads to ectopic trichome development. Expression of ovoB has additional effects on leg development (e.g. a bending of the proximal femur), while expression of tal also leads to the development of ectopic bristles on the femur (arrowheads in H).