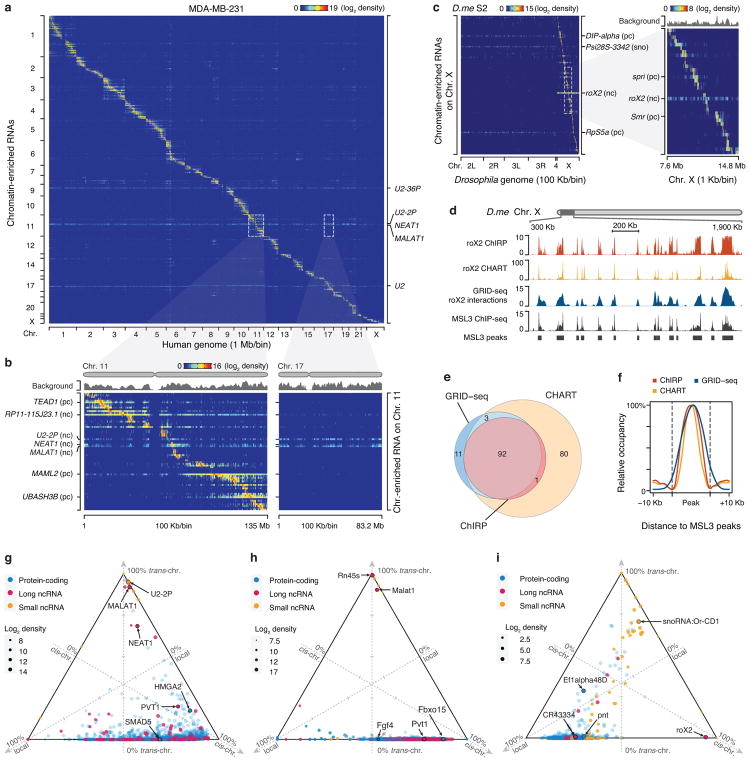
Fig. 2. Global view of RNA-chromatin interactions.
a, Heatmap showing chromatin-enriched RNAs across the whole human genome in MDA-MB-231 cells. Row: chromatin-enriched RNAs. Column: human genome in 1 Mb resolution. Major trans-chromosomal interacting RNAs are labeled on the right. U2-36P and U2-2P are transcripts from two pseudo U2 snRNA genes. b, Two enlarged representative regions boxed in a, showing detailed RNA-chromatin interaction patterns on Chr. 11 (left) and Chr. 17 (right) at 100 Kb resolution. pc: protein-coding RNAs, nc: non-coding RNAs. c, Heatmap showing background-corrected RNA-chromatin interactions on Chr. X across the Drosophila genome. Right: an enlarged view of the boxed region on the left, showing decoration of roX2 RNA on Chr. X in Drosophila S2 cells. d, A region of Drosophila Chr. X, illustrating roX2 RNA on chromatin detected by ChIRP and CHART in comparison with GRID-seq signals as well as ChIP-seq signals for the roX2 binding protein MSL3. e, Overlaps of peaks identified by different methods. f, Meta-analysis of roX2-chromatin interactions detected by ChIRP, CHART and GRID-seq relative to MSL3 ChIP-seq peaks. g,h,i Ternary plots of chromatin-enriched RNAs in called peaks in human MDA-MB-231 cells (g), mESCs (h), and Drosophila S2 cells (i), showing percentages of individual chromatin-interacting RNAs engaged in local (±1 Kb around their genes), cis (in the same chromosome except local), and trans (in other chromosomes) interactions. The 3 axes were shown as dashed lines perpendicular to the edges of the triangle. The arrowhead on the tip of each axis indicates the direction of increase from 0 (at the edge) to 100% (at the vertex). 3 ticks on each axis mark 25%, 50% and 75% positions. Colors of dots represent different types of RNAs and sizes represent chromatin interaction levels. Labeled are representative coding mRNAs and lncRNAs in each genome.