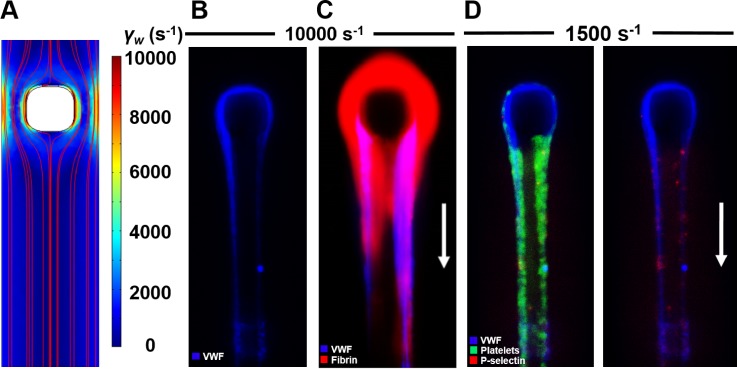
FIG. 2.
Impingement-post microfluidic device enables the study of coagulation and platelets on fibrous VWF. (a) COMSOL simulation shows the increased shear rate around the micropost even at relatively low inlet shear rates (1000 s−1). (b) EDTA-anticoagulated PFP was perfused at inlet shear rates of >5000 s−1, resulting in the formation of VWF fibers upstream, which hatch on the micropost and are held there by fluid forces. (c) Following VWF fiber formation, coagulable PFP was perfused over the VWF fiber, resulting in local fibrin formation. (d) When PPACK/Apixaban-inhibited WB was perfused over already formed VWF fibers, platelets rolled and firmly adhered to the VWF surface, resulting in some shear-induced platelet activation, as marked by P-selectin.