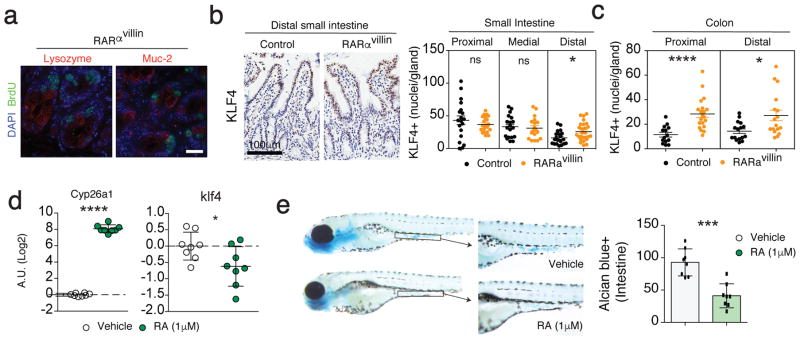
Figure 3.
RARα modulates differentiation within the secretory branch through KLF4. (a) Proliferative cells were identified by BrdU incorporation in parallel with lysozyme or muc-2 to detect paneth cells (left) and goblet cells (right), respectively. (b–c) KLF4 expression was measured in the distal small intestine (b) and colon (c) by immunohistochemistry and number of positive nuclei were counted per intestinal gland. 7–10 crypts were counted per intestine section in 2 mice per genotype. (d) RT-qPCR analysis of RAR target gene cyp26a1 and the transcription factor klf4 in zebrafish embryos treated with either vehicle or 1μM RA from 72 hours post-fertilization (hpf) till 108 hpf. Each dot represents a pool of 20 embryos. The mRNA expression was normalized to that of ef1α. (e) Whole-mount alcian blue staining of zebrafish embryos treated with either vehicle or 1μM RA from 72 hpf till 108 hpf (images). The graph represent quantification of alcian blue positive cells per intestine (n=8 per group). *P < 0.05; *** P < 0.005; **** P < 0.001 Student’s t-test. Error bars represent SEM. Scale bar; 20 μm (a), 100 μm (b)