Figure 2.
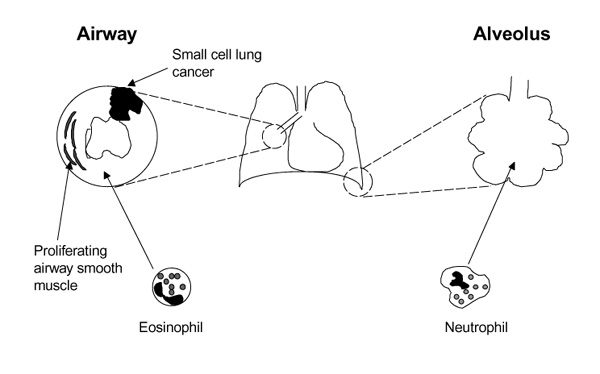
PI-3K in respiratory disease. Within the airway, activation of PI-3K is thought to contribute to the proliferation of smooth muscle and the accumulation of eosinophil characteristic of asthma, and to the mitogenesis and prolonged survival of small cell lung cancer cells. PI-3K-dependent neutrophil extravasation and activation have been implicated in the pathogenesis of multiple respiratory diseases including ARDS, pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary vasculitides and bronchiectasis.
