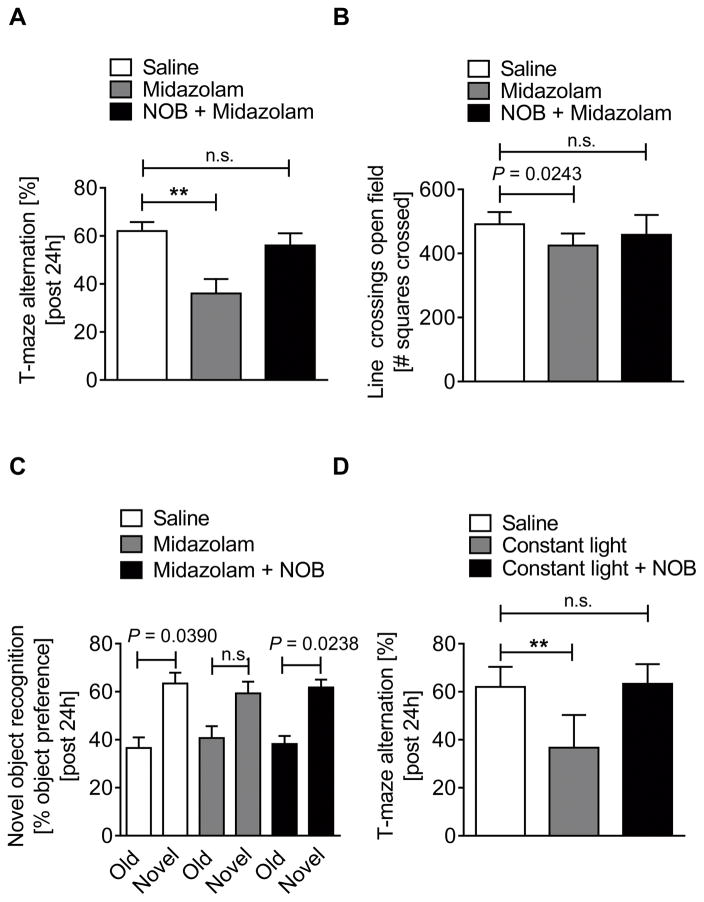
Figure 5. Nobiletin abolished midazolam or constant light induced cognitive deficits.
Wildtype (C57BL6/J) mice were injected with either midazolam (10 mg/kg i.p.) or midazolam + nobiletin (1 mg/kg i.p.) and compared to saline treated controls. 24 hours later mice underwent behavioral studies. In a subset of experiments mice were exposed to 7 days of constant light and tested for behavioral changes 24h later. (A) T-maze alternation in % 24 hours after a single dose of midazolam or midazolam + nobiletin. (B) Numbers of squares crossed for 10 minutes (line crossing) 24 hours after a single dose of midazolam or midazolam + nobiletin. (C) Preference in % for a novel object after 2 days habituation to two old objects 24 hours after a single dose of midazolam or midazolam + nobiletin. (D) T-maze alternation in % 24 hours after 7 days at constant light conditions with and without nobiletin. All data on behavioral tests have n=5 individual wildtype mice and are presented as mean ± SD, NOB=nobiletin, P value denotes t-test and * denotes one-way ANOVA (see also Supplemental Digital Content 1).