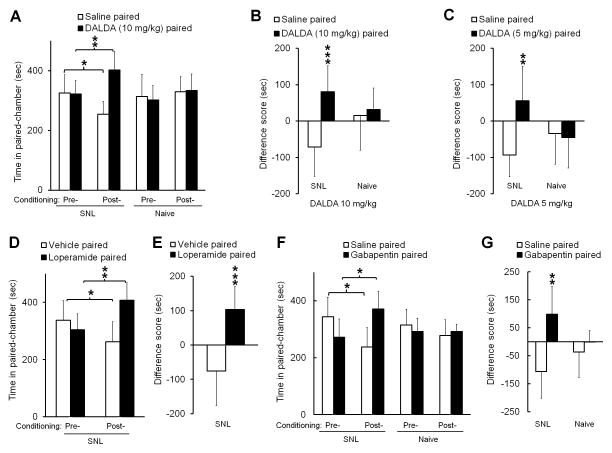
Figure 1. Systemic administration of peripherally acting mu-opioid receptor agonists induces conditioned place preference (CPP) in nerve-injured rats.
(A) SNL rats spent more time in a DALDA-paired chamber after drug conditioning (10 mg/kg, s.c., n=9) than during the preconditioning test period. However, DALDA did not induce CPP in naive rats (n=8). (B) In SNL rats, the difference score (post-conditioning time – pre-conditioning time) for the DALDA-paired chamber (n=9) was significantly greater than that for the saline-paired chamber. (C) A lower dose of DALDA (5 mg/kg, s.c., n=8) also significantly increased the difference score for the DALDA-paired chamber in SNL rats, but not naïve rats (n=8). (D) Loperamide (5 mg/kg, s.c., n=8), another peripherally acting opioid, induced CPP in SNL rats. (E) The difference score for the loperamide-paired chamber was significantly greater than that for the vehicle-paired chamber. (F) SNL rats spent more time in chambers paired with gabapentin (60 mg/kg, i.p., n=8) after drug conditioning than they did before conditioning. However, gabapentin did not induce CPP in naive rats (n=8). (G) The difference score for the gabapentin-paired chamber was significantly greater than that for the saline-paired chamber. A, D, F: Two-way repeated measures ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test, *P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01. B, C, E, G: Student’s t-test, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 versus saline-paired. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. ANOVA, analysis of variance; DALDA, dermorphin [D-Arg2, Lys4] (1–4) amide; i.p., intraperitoneal; s.c., subcutaneous; SNL, spinal nerve ligation.