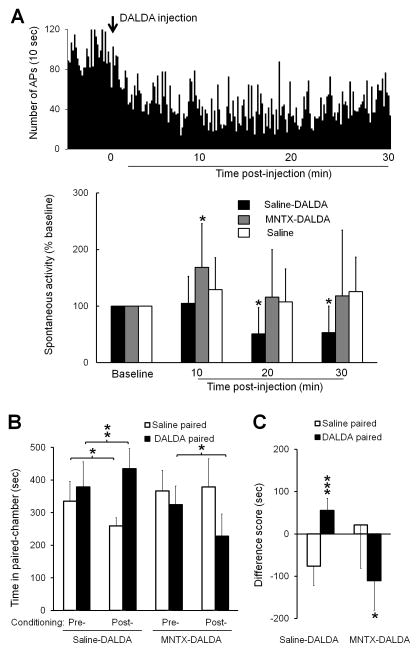
Figure 5. Effects of methylnaltrexone on spontaneous activity of dorsal horn neurons and CPP to dermorphin [D-Arg2, Lys4] (1–4) amide (DALDA) in nerve-injured rats.
(A) Upper: Peri-stimulus time histogram shows the spontaneous activity of a WDR neuron in an SNL rat before and 0–30 min after DALDA treatment (10 mg/kg, s.c.). Bin size: 10 s. Lower: The spontaneous activity rates of WDR neurons in SNL rats were significantly decreased at 20 and 30 min after treatment with DALDA (10 mg/kg, s.c., n=8), but not saline (n=8). The inhibitory effect of DALDA was blocked by methylnaltrexone (5 mg/kg, n=9, i.p., 10 min pretreatment). Two-way mixed-model ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test, *P < 0.05 versus baseline. (B) Pretreatment with methylnaltrexone (5 mg/kg, n=9, 10 min, i.p.), but not saline (n=7), blocked CPP to DALDA (10 mg/kg, s.c.) in SNL rats. (C) The difference scores of time spent in the DALDA-paired and saline-pared chambers. Two-way repeated measures ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 versus the indicated group or the saline-paired chamber. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. ANOVA, analysis of variance; APs, action potentials; CPP, conditioned place preference; i.p., intraperitoneal; MNTX, methylnaltrexone; s.c., subcutaneous; SNL, spinal nerve ligation; WDR, wide-dynamic range.