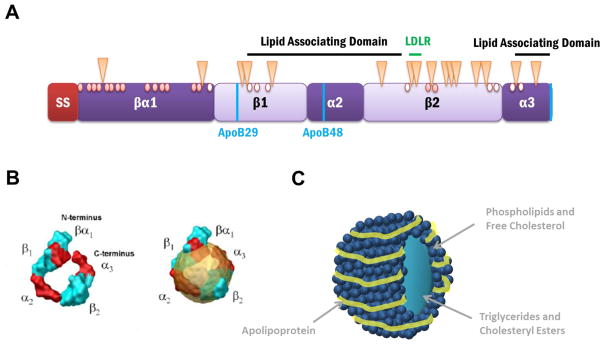
Figure 2. Proposed Structural Domains and Modifications of ApoB.
(A) The predicted apoB domain structure contains a 27 amino acid signal sequence (SS), which targets apoB to the ER membrane and allows for translocation or entry into the ER, and a β-barrel domain, which is directly followed by α-helix, β-sheet, α-helix motifs, and is interspersed by 2 lipid association domains. The naturally occurring isoforms, apoB100 and apoB48, and the hypolipidemic truncation, apoB29, are depicted using vertical blue lines. The LDL receptor binding region is found in the β2 domain and is indicated with a horizontal green line. The 16 glycosylated asparagine residues in apoB are indicated with triangles. Of the 25 cysteines, only 16 participate in disulfide bond formation (red circles) while the remaining 9 are free sulfhydryls (open circles).
(B) Computer simulated model of proposed apoB structure (left) alone and (right) in a lipoprotein. The image is reproduced with permission from [49].
(C) A representation of a lipoprotein particle. The apolipoprotein wraps around the circumference of the lipoprotein which consists of phospholipids, free cholesterol, triglycerides, and cholesteryl esters.