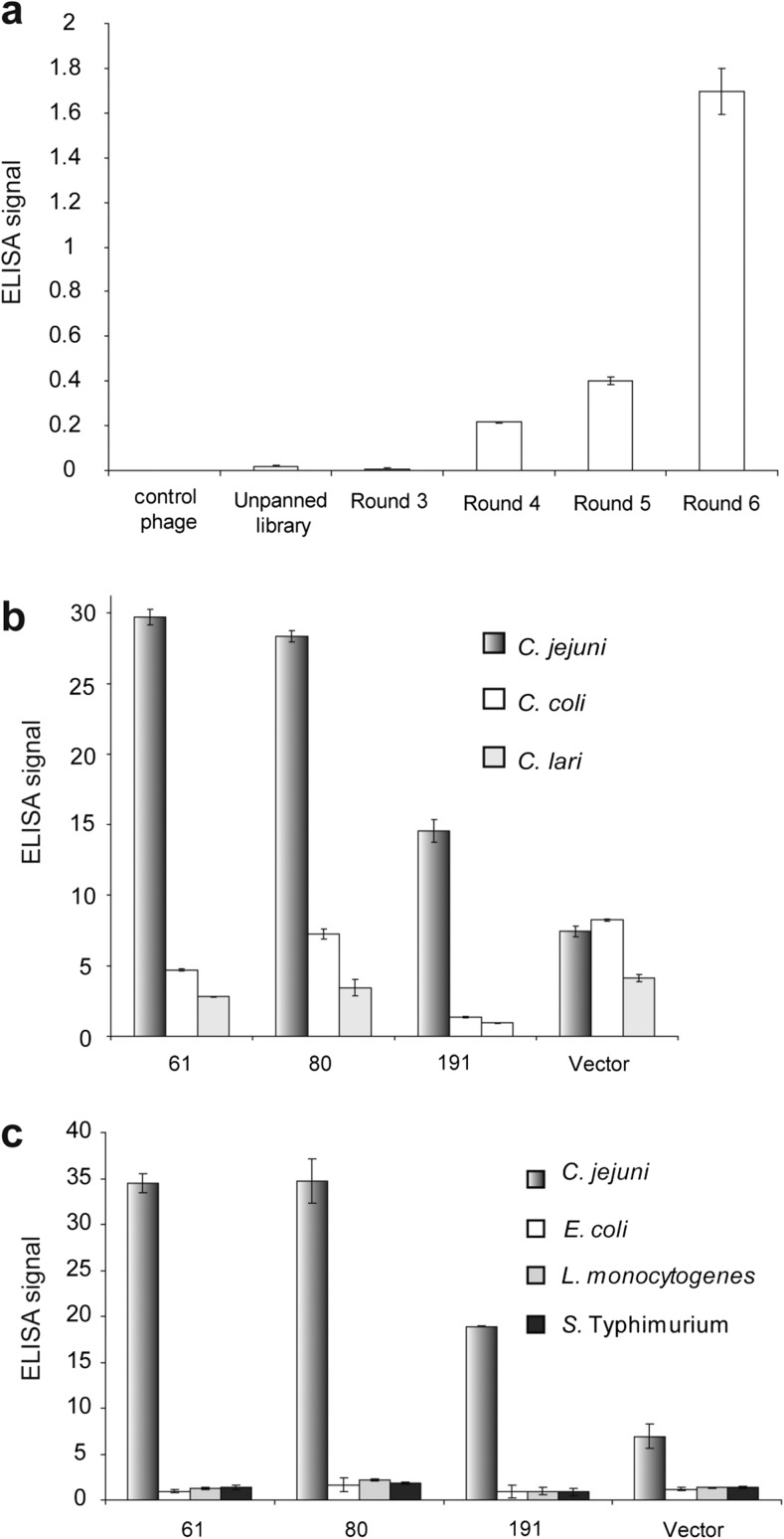
Fig. 2.
Enrichment of C. jejuni-binding scFv-displaying phages by biopanning and characterization of selected phage clones for binding specificity. In a–c equal amount of cells and phage particle were used in each experiment. The bound phage particles were detected using HRP-conjugated anti-M13 antibody and the substrate ABTS. a ELISA assay to test binding activity to C. jejuni cell, using scFv-displaying phage pools that resulted from different rounds of biopanning. The control phage is the non-displaying phage. Signal reading at 415 nm is shown in the Y-axis. b The three best scFv-displaying phage clones (scFv 61, scFv 80, scFv 191) were tested in ELISA assay for their binding activity to C. jejuni and other Campylobacter spp. c The three best scFv-displaying phage clones were tested in ELISA assay, comparing their binding activity to C. jejuni and three non-Campylobacter bacterial cells. In b, c, the signal reading at 415 nm of the cell-coated wells was normalized against that in the uncoated wells. Each column and error bar in a–c represents the mean and standard deviation of triplicates of reactions