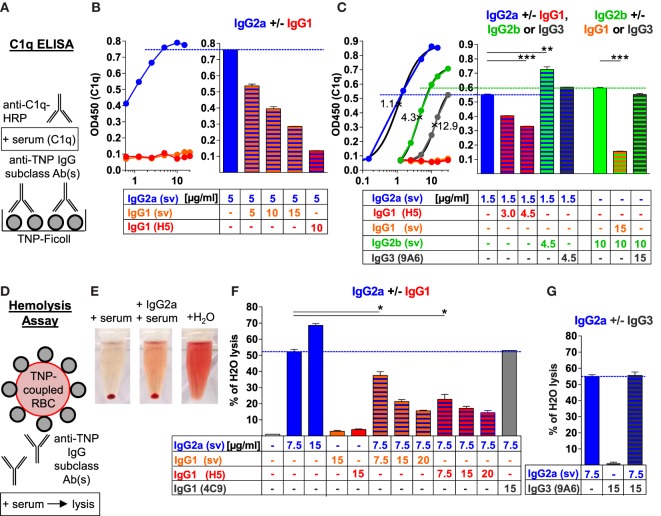
Figure 1.
Murine IgG1 prevents C1q binding and complement activation by IgG2a, IgG2b, or IgG3 antibodies (Abs) in an antigen-specific manner. (A) Schematic description of the C1q ELISA applied in panels (B,C) and Figure S1 in Supplementary Material. 2,4,6-Trinitrophenyl (TNP)-Ficoll-coupled 96-well plates were incubated with different concentrations of one or two anti-TNP monoclonal IgG subclass Abs [anti-TNP IgG1 (clone H5; red), IgG3 (clone 9A6; gray) as well as IgG1 (orange), IgG2a (blue), and IgG2b (green) class-switch variants (sv; with identical VDJ sequences)] and subsequently with C1q-containing serum; C1q was detected with an anti-C1q-HRP-coupled secondary Ab system. (B,C) Mean of the resulting C1q ELISA values measured at 450 nm (OD450) with the indicated (μg/ml) single or paired anti-TNP IgG subclass Abs (n = 2). IgG subclass-specific half-maximal effective concentrations (EC50; ×) were calculated by the interpolated subclass-specific C1q-binding curves in panel (C) (R2 > 0.99). (D) Schematic description of the applied red blood cell (RBC)-lysis assay. TNP-coupled RBCs (Figure S1E in Supplementary Material) were incubated with one or two anti-TNP monoclonal IgG subclass Abs or an anti-ovalbumin IgG1 (clone 4C9) Ab and subsequently treated with serum containing C1q and further complement components. (E) Exemplary hemolysis approach with centrifuged TNP-coupled RBCs after reaction with serum, serum plus anti-TNP IgG2a or H2O as a positive control (100% lysis). (F,G) Mean of the resulting RBC lysis [measured hemoglobin (OD 414 nm) in the supernatant of centrifuged RBCs], which was calculated as the percentage of H2O-induced positive control RBC lysis (100%; maximum of the y-axes) with the indicated (μg/ml) single or paired IgG subclass Abs (n = 2). The results from one of at least two independent experiments are presented.