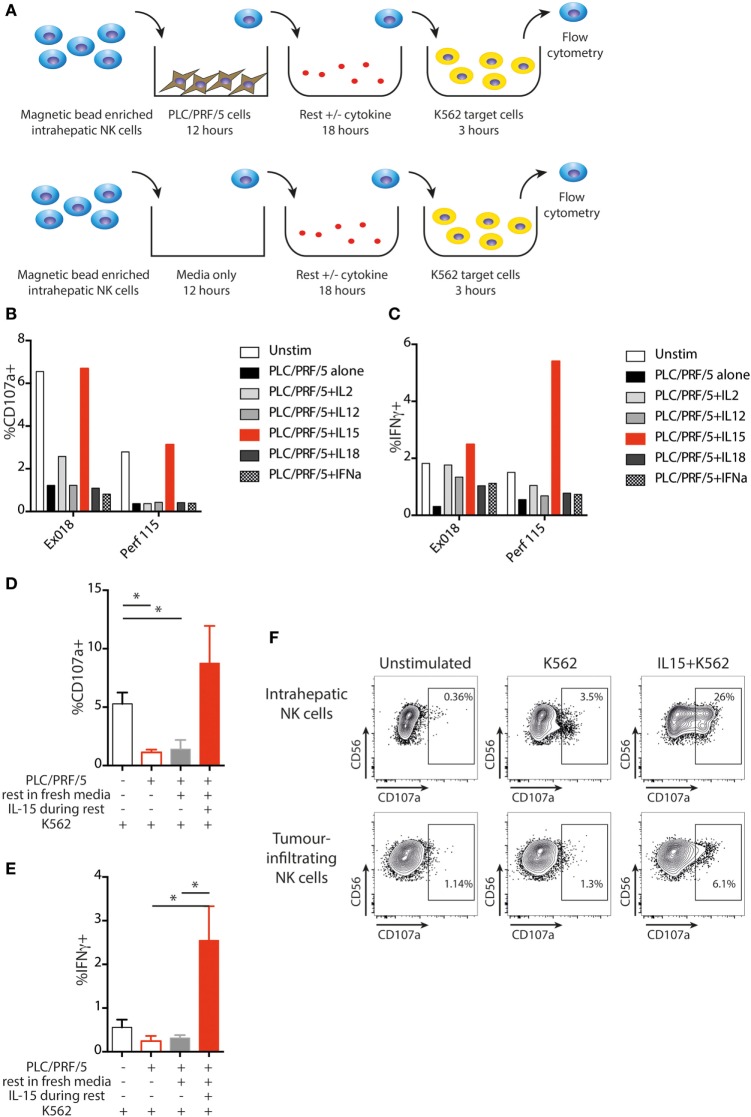
Figure 7.
IL-15 restores NK cell function following PLC/PRF/5 coculture. (A) Diagram showing experimental design of PLC/PRF/5 coculture followed by rest in fresh media ± cytokine before K562 challenge. (B) CD107a staining following K562 challenge after PLC/PRF/5 coculture, then rest overnight in fresh media ± the indicated cytokine using intrahepatic NK cells isolated from a liver explant (Ex) and from a liver perfusate (Perf). (C) Intracellular IFNγ staining following K562 challenge after PLC/PRF/5 coculture, then rest overnight in fresh media ± the indicated cytokine using intrahepatic NK cells isolated from a liver explant (Ex) and from a liver perfusate (Perf). (D) Summary data showing CD107a staining following K562 challenge of intrahepatic NK cells unstimulated, after PLC/PRF/5 coculture, after PLC/PRF/5 coculture then rest in fresh media and after PLC/PRF/5 coculture then rest in IL-15 containing media (n = 5 liver samples). (E) Summary data showing intracellular IFNγ staining following K562 challenge of intrahepatic NK cells unstimulated, after PLC/PRF/5 coculture, after PLC/PRF/5 coculture then rest in fresh media and after PLC/PRF/5 coculture then rest in IL-15 containing media (n = 5 liver samples). (F) Example of CD107a staining on paired intrahepatic and tumor-infiltrating NK cells following K562 challenge after overnight rest with IL-15. Groups were compared using unpaired t test with Welch’s correction. p ≤ 0.05 was considered to be significant for all tests. Figures are labeled: *p ≤ 0.05.