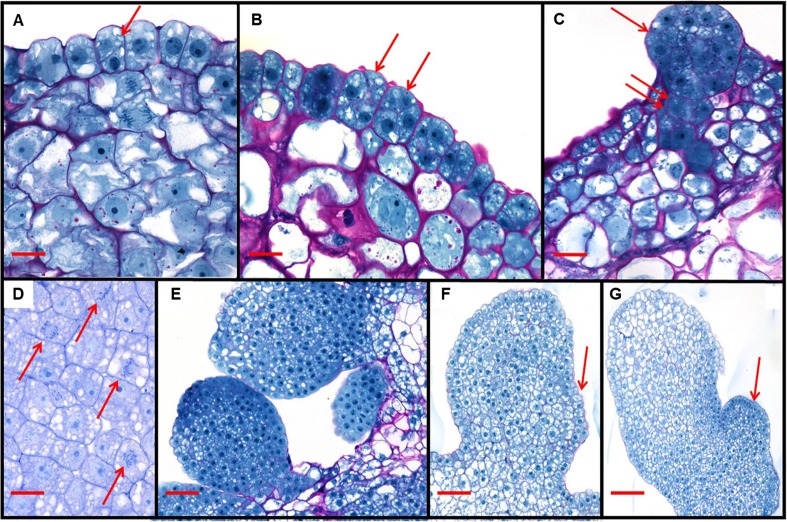
Figure 5.
Histology of Zea mays L. somatic embryo development after A. tumefaciens-mediated transformation of immature embryos with a T-DNA containing the expression cassettes Zm-Axig1pro::Wus2 plus Zm-PLTPpro::Bbm. The earliest morphological change observed were transverse or oblique cell divisions (arrow, A), continuing to divide and become multicellular (arrows, B) and growing into early globular pro-embryos (arrow, C) with some being subtended by what appeared to be a suspensor (double arrow, C). In the developing somatic embryos, multiple mitotic figures were often observed in the same cross-section (arrows, D). In E, multiple independent somatic embryos were observed in close proximity, and as somatic embryos continued to develop, the embryonic meristem could be observed to develop (arrows, F, G). Scale bar: A 12 μm; B–D 25 μm; E, F 50 μm; G 100 μm