Fig. 2.
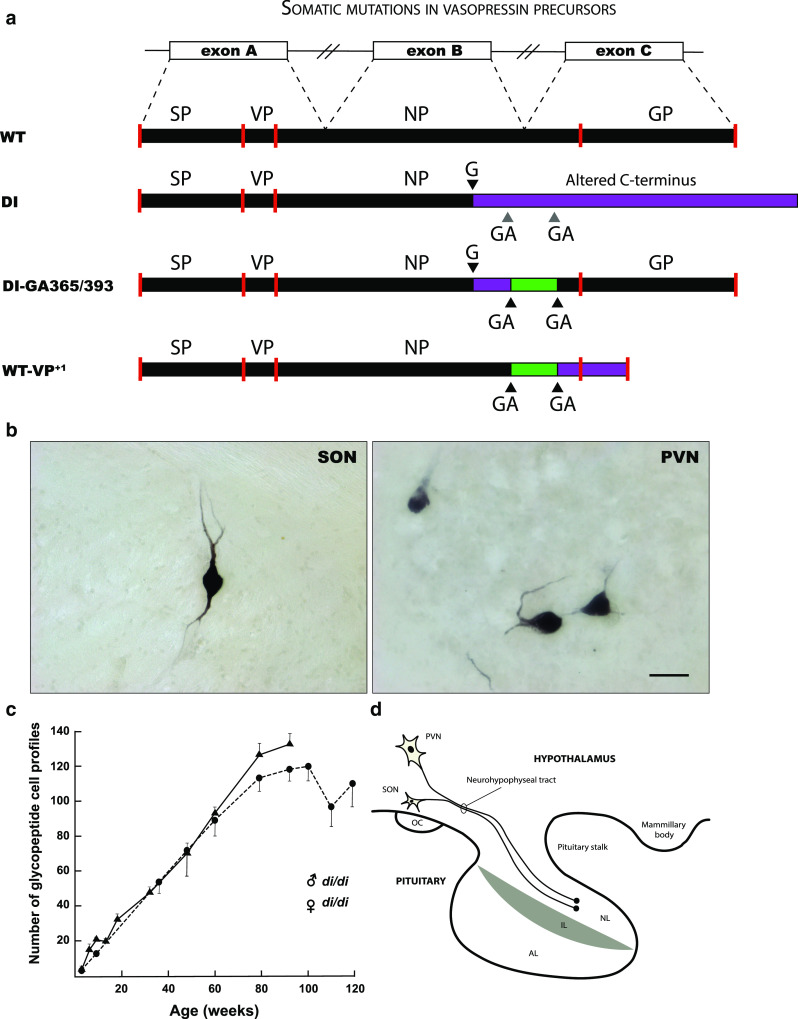
Mutations in post-mitotic vasopressin neurons. a Schematic representation of the vasopressin (VP) gene, VP prohormone and mutant forms. The VP gene consists of three exons (exon A, B, and C, consisting of 429 nucleotides), which give rise to a transcript that is spliced to generate the mRNA template for a precursor protein (WT). VP precursor protein is translated in the endoplasmatic reticulum (ER), post-translationally processed and packaged within neurosecretory granules. Subsequently, the protein is axonally transported to nerve terminals in the neural lobe of the pituitary gland (d). In the homozygous (di/di) Brattleboro rat, a single base (G) deletion in exon B results in an out-of-frame protein that contains a poly-lysine tail that cannot be properly processed (DI). This results in (central) diabetes insipidus (DI), a condition that is characterized by polyuria and polydipsia, due to the inability to effectively regulate the VP-mediated retention of water in the kidney’s collection ducts (antidiuretic function). This is an autosomal recessive trait that is inherited in a simple Mendelian fashion. b Intriguingly, some solitary neurons in the supraoptic nucleus (SON) and paraventricular nucleus (PVN) of the homozygous Brattleboro rat appear to be immunoreactive for VP. Bar = 50 μm (Verheijen, Vermulst and van Leeuwen, unpublished). This appears to be due to a second mutation (ΔGA) in a GAGAG motif that is located downstream of the single base mutation (a). As a result the VP mutant precursor (DI-GA365/393) can be processed (i.e., the glycoprotein (GP)-containing part) and the neurosecretory granules can be axonally transported towards the neural lobe. The amount of reverted neurons (+/di) increases age-dependently in both male (filled triangle) and female (filled circle) rats (c). Because GAGAG motifs are also present in the wild-type VP gene of rat and human, a similar process can take place and convert the wild-type VP precursor into an aberrant one (WT-VP+1). This has been shown to occur in hypothalamus of both rat and human. AL anterior lobe, IL intermediate lobe, NL neural lobe, NP neurophysin, OC optic chiasm, SP signal peptide
