Fig. 3.
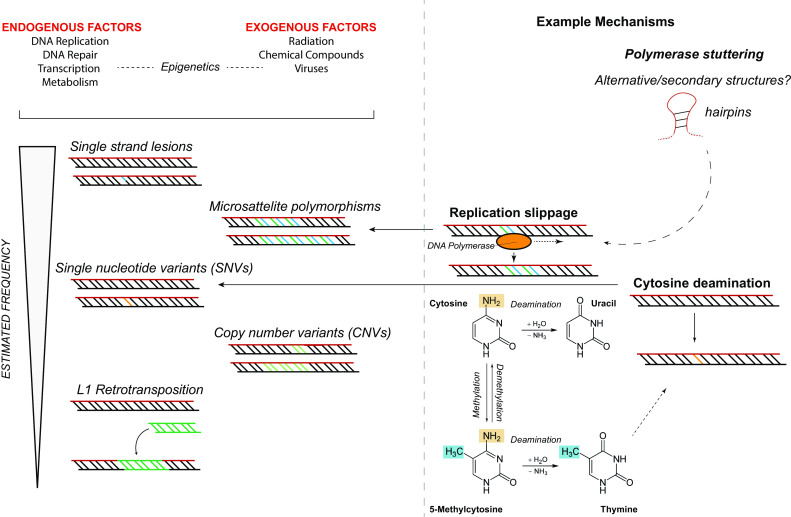
Various types and mechanisms of neuronal somatic mutations. Different types of mutations have been found to be present in single neurons, including long interspersed nuclear element 1 (L1 or LINE1) retrotransposition, copy-number variations (CNVs), single-nucleotide variants (SNVs), and microsatellite/short tandem repeat variants. The exact contribution of each of these events to somatic neuronal mosaicism is unknown. Also, the mechanisms through which these mutations can arise are mostly unknown. Slippage of DNA polymerases, e.g., due to secondary structures in the chromatin, can cause changes in length of microsatellites. Cytosine deamination has been recognized as a frequent cause of SNVs. It will be necessary to accurately quantify these different types of mutations, for various cell types and brain regions, during different developmental stages or under particular conditions, in order to gain insight into their (potential) roles
