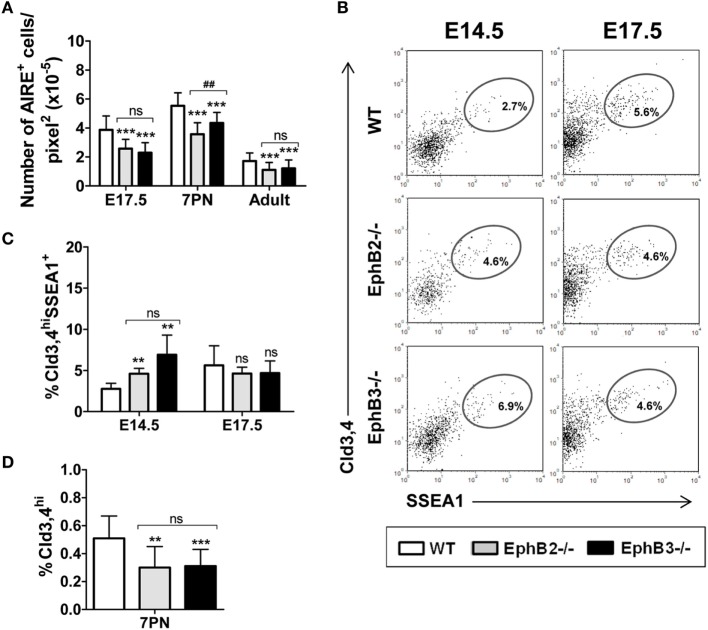
Figure 4.
Presence of AIRE+ cells and Cld3,4+ cells in fetal, postnatal, and adult wild type (WT) and EphB-deficient thymi. (A) Semi-quantitative analysis of AIRE+ cells reveals that mutant thymi have significantly lower numbers of these cells at all studied stages. (B) Dot plots show the expression of Cld3,4hiSSEA1+ medullary TECs progenitor cells in both WT and EphB-mutant thymi at E14.5 and E17.5, indicating their frequencies. (C) Comparative analysis of the proportions of Cld3,4hiSSEA1+ cells in WT and EphB-deficient thymi at E14.5 and E17.5. (D) Semi-quantitative analysis of the Cld3,4hi expression in WT and mutant thymi at 7PN. The significance of the Student’s t-test probability is indicated: **p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.005; and ##p ≤ 0.01 between mutants; ns, non-significant.