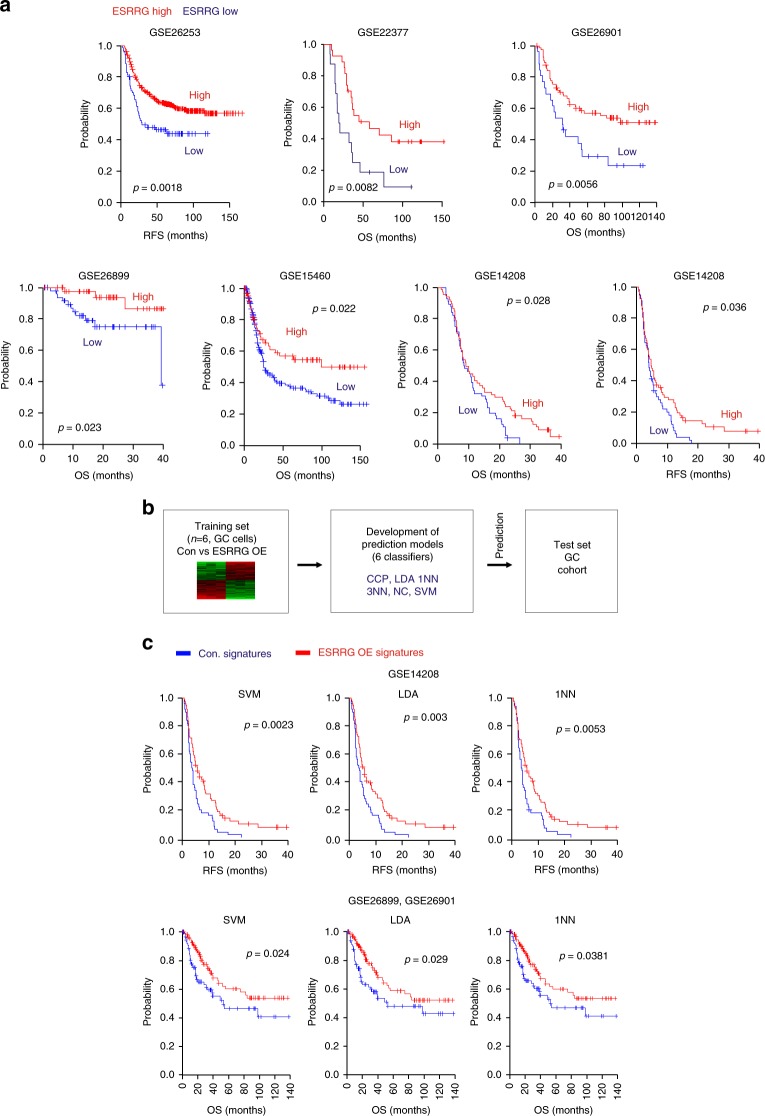
Fig. 3.
Clinical relevance of ESRRG in GC patient prognosis. a Patients in the indicated GC cohorts were dichotomized by relatively high or relatively low ESSRG expression and were considered for plotting. b, c Establishment of gene expression profiles of ESRRG downstream targets. b Gene expression signature of ESRRG in control (Con.) or ESRRG lentivirus transduced AGS cells. Genes in the Venn diagram were selected by applying a two-sample Student’s t-test (p < 0.001) to compare Con. and ESRRG OE samples. b Overall scheme of prediction models and evaluation of predicted outcome based on a shared gene expression signature of ESRRG in GC cell lines. The ESRRG gene expression signature was used to form a series of classifiers that estimated the probability of how much the expression pattern of a particular patient with GC was similar to the shared signature; control (Con.) vs. ESRRG OE (over-expression). c Kaplan–Meier plots of OS of GC patients in the GSE26899 cohort merged with the GSE26901 and GSE14208 cohorts were used to predict outcome based on the Con. and ESRRG OE signatures as a classifier. The differences between groups were significant where indicated (log‐rank test). SVM, support vector machines; LDA, linear discriminator analysis; 1NN, one nearest neighbors