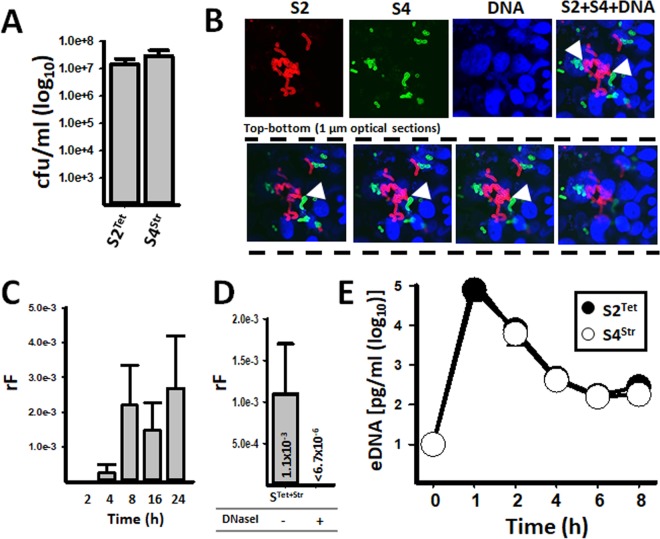
FIG 1 .
Rapid recombination of antibiotic resistance genes within pneumococcal biofilm consortia. Strains SPJV17 (S2Tet) and SPJV23 (S4Str) were inoculated into a bioreactor and incubated at ~35°C. After 8 h of incubation, (A) the density (CFU per milliliter) of each strain was obtained by culture in BAPs with the appropriate antibiotic, or (B) consortial biofilms were fixed with 2% PFA, stained with antiserotype-specific Alexa 555-labeled (S2) or Alexa 488-labeled (S4) antibodies, and the DNA was stained with DAPI. Preparations were analyzed by confocal microscopy. The top panels show xy optical middle sections of the indicated channel, or the merge, whereas bottom panels show representative xy 1-µm optical sections of a total of ~10 µm sectioned from top through bottom. (C) The recombination frequency (rF) of double-resistant pneumococci was obtained at each time point. (D) Bioreactor chambers were incubated for 8 h in the presence of 20 U/ml of DNase I (+) or left untreated (−), after which bacteria were counted and the rF was calculated. (E) Extracellular DNA (eDNA) was purified from supernatants collected from bioreactor chambers at the indicated time. The DNA was used as a template in serotype-specific qPCRs amplifying eDNA from either S2Tet or S4Str. In panels A and C to E, error bars represent the standard errors of the means calculated using data from at least three independent experiments.