FIG 7 .
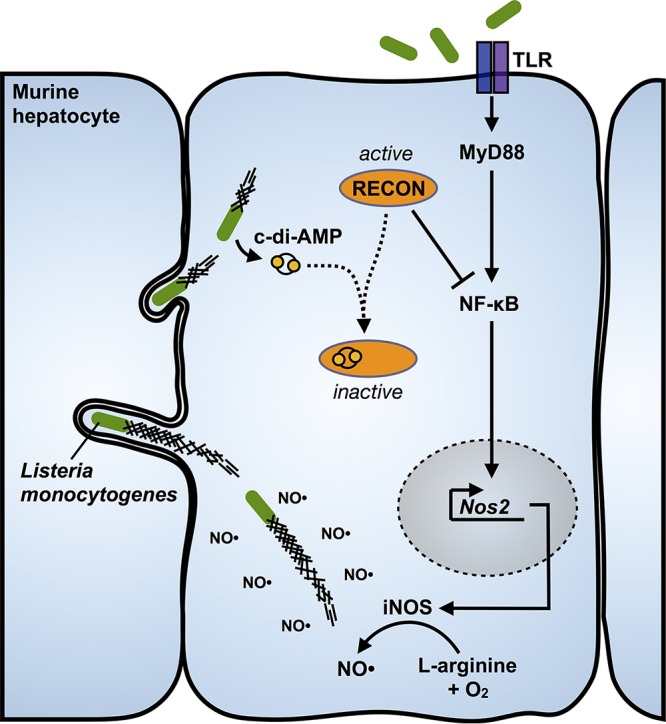
Inhibition of RECON by c-di-AMP promotes L. monocytogenes intercellular spread via increased nitric oxide. During infection, L. monocytogenes secretes c-di-AMP into the cytosol, which is then bound by RECON. Inhibition of RECON’s enzymatic activity by c-di-AMP releases a brake on NF-κB activation downstream of TLR engagement. The augmentation of NF-κB activation leads to increased iNOS levels and nitric oxide production. Elevated nitric oxide promotes elongation of L. monocytogenes actin tails, increased bacterial speed in the cytosol, and enhanced cell-to-cell spread.
