Fig. 6. Performance evaluation of infrared memory.
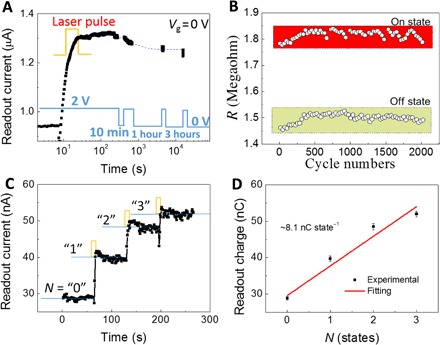
(A) Charge storage stability. The infrared pulse intrigues a persistent photocurrent state. The readout current fully retains its original state even if the device is powered off for 10 min and 1 or 3 hours. The inset at the bottom of (A) shows time-dependent bias voltage Vsd for reading the states. (B) Endurance of optical writing and electrical erasing operation. The on and off states are hardly changed during the entire 2000 cycles. (C) Four states are continuously programed by multiple laser pulses with a wavelength of 1940 nm, laser pulse intensity of 27 μW cm−2, and duration of 1 s. The readout current increases with the number of laser pulses. Four resistance states are numbered as “0,” “1,” “2,” and “3.” (D) The readout charge collected for 1 s is nearly linearly dependent on the resistance states.
