Figure 2.
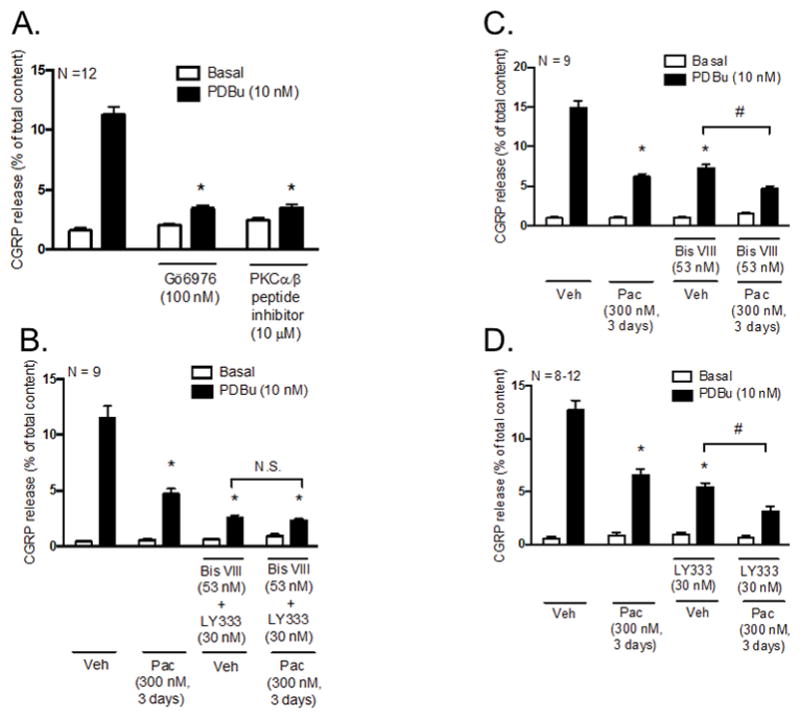
Inhibition of PKCα and PKCβI/II activity mediates the decrease in PDBu-stimulated CGRP release following chronic exposure to paclitaxel in cultured sensory neurons. Each column represents the mean ± SEM of basal (white columns) or PDBu-stimulated (black columns) CGRP release expressed as % of total content in the absence and presence of PKCα and PKCβI/II inhibitors. (A) Naïve cultures were pre-treated with Gö6976 (100 nM) or a myristoylated PKCα/β peptide inhibitor (10 μM) for 10 minutes prior to stimulation with PDBu (10 nM). An * indicates a significant decrease in PDBu-stimulated release in neurons pre-treated with Gö6976 or the myristoylated PKCα/β peptide inhibitor (p < 0.05, N = 12). Cultures were exposed to 300 nM paclitaxel for 3 days prior to stimulation with PDBu (10 nM) in the presence and absence of the (B) PKCα inhibitor (Bis VIII; 53 nM) + PKCβI/II inhibitor (LY333531; 30 nM), (C) Bis VIII or (D) LY333531. An * indicates a significant decrease in PDBu-stimulated release in paclitaxel-only treated neurons, vehicle- and paclitaxel-treated neurons pre-treated with (B) Bis VIII + LY333531, (C) Bis VIII or (D) LY333531 compared to vehicle-only treated neurons and a # indicates a significant decrease in PDBu-stimulated release in paclitaxel-treated neurons compared to vehicle-treated neurons pre-treated with (C) Bis VIII or (D) LY333531. Significance was determined using a two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test (p < 0.05, N = 8–12). Veh - Vehicle; Pac - Paclitaxel; LY333 – LY333531; N.S. – not significant.
