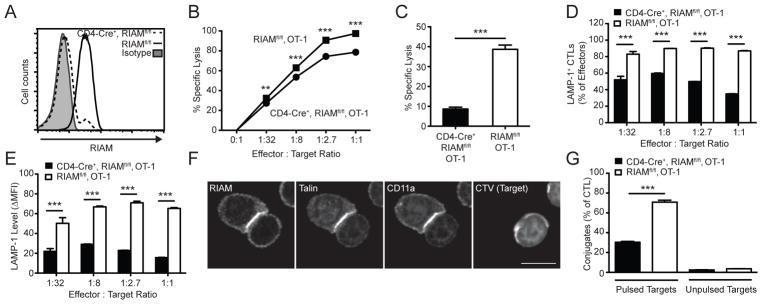
FIGURE 4. RIAM mediates CTL function.
OT-1 splenocytes were differentiated to CTL by culture with SIINFEKL peptide and IL-2. (A) RIAM deletion in CTL. RIAM expression in OT-1 CTL was measured by intracellular staining and flow cytometry. (B) In vitro target lysis. CTL were cultured overnight with a mixture of SIINFEKL-pulsed (CFSElo) and unpulsed (CFSEhi) target splenocytes; lysis was detected by flow cytometry; performed twice. (C) In vivo target lysis. CTL were injected i.v. into recipient C57BL/6 mice, which received a mixture of SIINFEKL-pulsed (CFSElo) and unpulsed (CFSEhi) target splenocytes 24h later. Recipient splenocytes were analyzed 4h later by flow cytometry for decrease in the % of pulsed targets; n=4 mice per group; performed twice. (D–E) In vitro degranulation. CTL were cultured with SIINFEKL-pulsed target splenocytes in the presence of anti-CD107a (LAMP-1), followed by staining for CD8 and flow cytometric analysis; performed twice. (F) RIAM localization to CTL immune synapses. CTL were allowed to form conjugates with SIINFEKL-pulsed splenocyte targets, fixed, stained with indicated antibodies, and visualized by confocal microscopy. Scale bar = 5 μm. (G) CTL-Target conjugate formation. CTL were labeled with CFSE and incubated with eFluor 670-labeled target SIINFEKL-pulsed splenocyte targets. The % conjugation was determined by flow cytometry; performed twice.