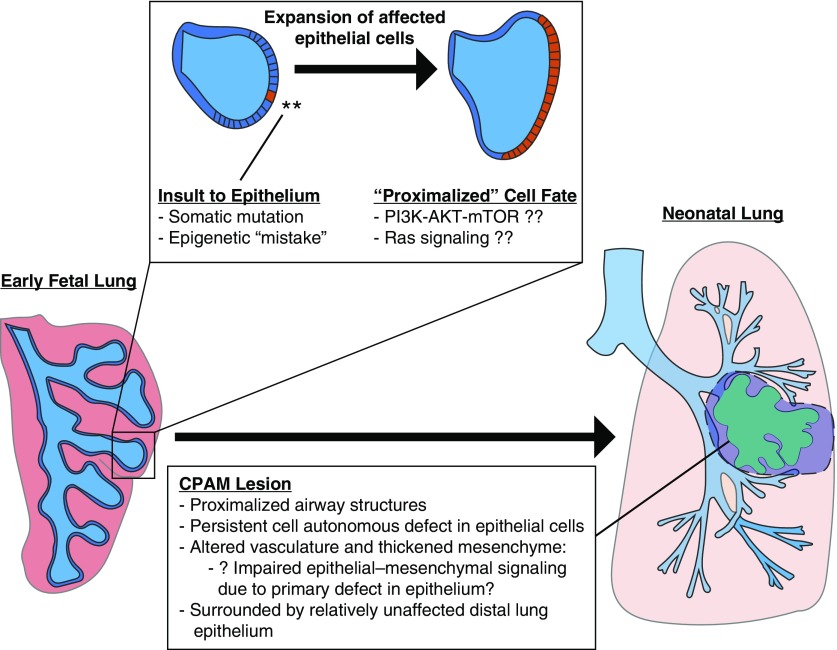
Figure 6.
Proposed model diagram. We propose that a defect occurs during branching morphogenesis of the lung, such as a somatic mutation or alteration in chromatin state, that results in dysregulation of a key developmental signaling pathway such as Ras/MAPK or PI3K–AKT–mTOR signaling. This impaired epithelial population expands as development proceeds and remains “proximalized,” forming an abnormal collection of cystic airway structures seen in the mature congenital lung lesion. Disrupted epithelial–mesenchymal interactions arising from these epithelial cells occasionally result in abnormal vascular development or may even “recruit” a systemic feeding vessel. CPAM = congenital pulmonary airway malformation; MAPK = mitogen-activated protein kinase; PI3K–AKT–mTOR = phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase–AKT–mammalian target of rapamycin.