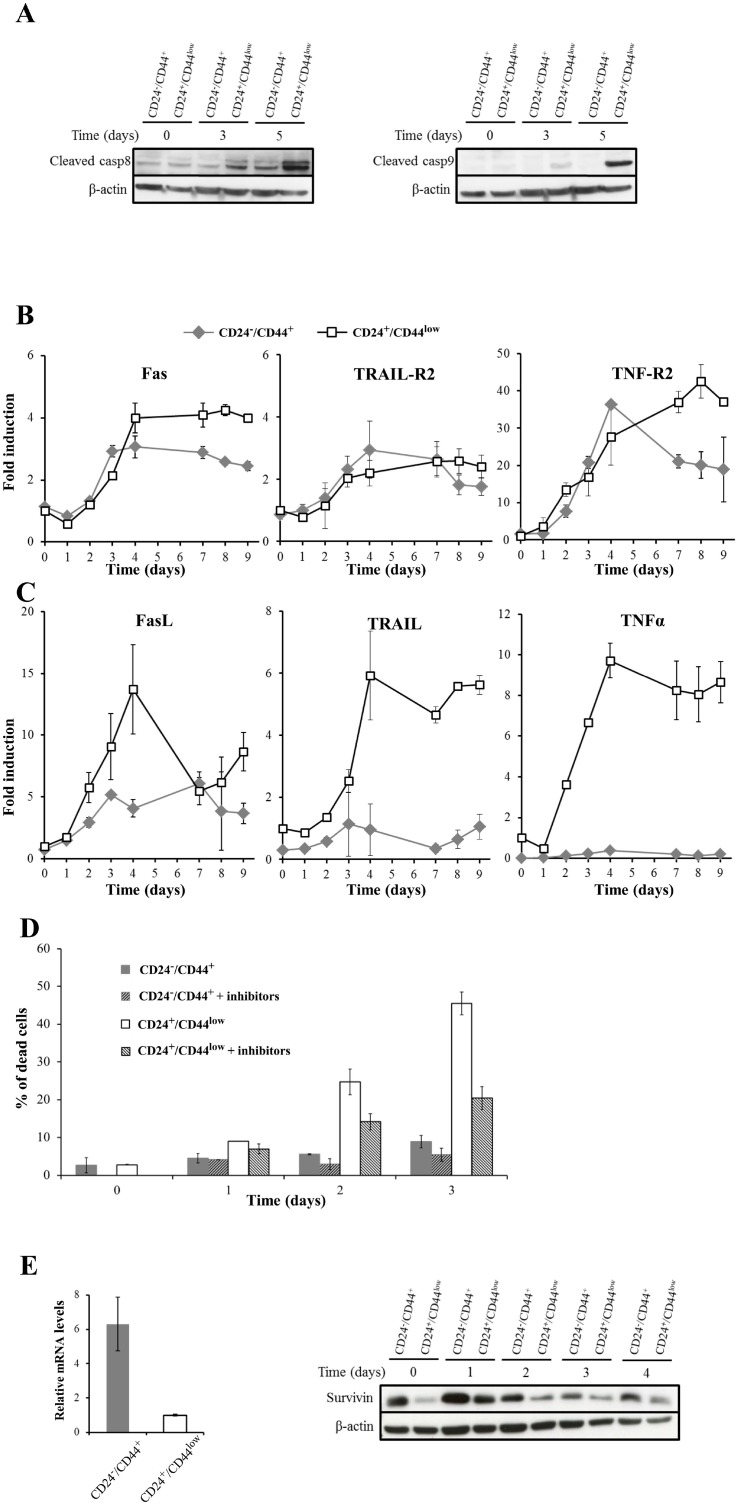
Figure 6. Role of death receptor pathways in radiation-induced cell death of CD24+/CD44low cells and CD24−/low/CD44+ cells.
(A) Kinetics of cleavage of caspases 8 and 9 at different times after 10 Gy irradiation. The Western blots shown are representative of 3 independent experiments. (B) and (C) mRNA levels of death receptors and corresponding ligands after a 10 Gy irradiation of CD24+/CD44low cells and CD24−/low/CD44+ cells. These mRNA levels were determined by quantitative RT-PCR. Normalization was performed as indicated in Materials and Methods and the basal expression of CD24+/CD44low cells on day 0 was normalized to 1. Each value corresponds to the mean value of at least 2 independent PCRs performed from 3 independent experiments. Error bars correspond to standard deviation. (D) Neutralization of the death receptor pathways reduces radiation-induced apoptosis. CD24+/CD44low cells and CD24−/low/CD44+ cells were 10 Gy-irradiated and treated or not with a combination of Fas/Fc, TRAIL-R1/Fc and TNF-R1/Fc chimera (250 ng/mL, 100 ng/mL and 100 ng/mL, respectively). These chimeras, which are cytokines designed to neutralize apoptosis induced by the corresponding ligand, were added to the culture medium at days 0 and 2. Viable and dead cells were counted after trypan blue staining. Results correspond to the mean ± standard deviation of 3 independent experiments. (E) Survivin expression by quantitative RT-PCR (left) and Western blot (right) after a 10 Gy irradiation of CD24+/CD44low cells and CD24−/low/CD44+ cells. For RT-PCR, normalization was performed as indicated above, and the Western blot shown is representative of 3 independent experiments.