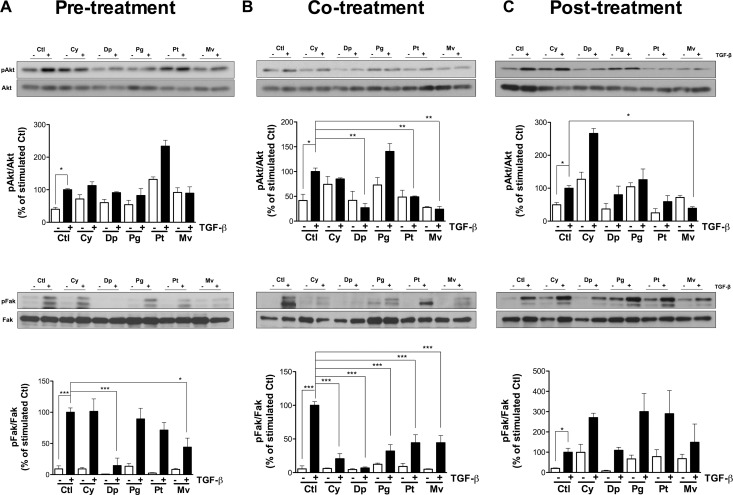
Figure 6. Anthocyanidins alter Akt and Fak signaling pathways.
U-87 MG cells were incubated in serum-free medium containing (or lacking) 50 μM of the indicated anthocyanidin. Cells were pre-treated with (A) anthocyanidins for 24 h, followed by 10 ng/mL TGF-β for 48 h, or (B) serum starved for 24 h and co-treated with anthocyanidins and TGF-β for 48 h, or (C) serum starved for 24 h followed by the addition of TGF-β for 48 h and post-treated with anthocyanidins for the last 24 h. After treatments, levels of phosphorylated Akt and Fak proteins, along with their individual total protein levels, were monitored by immunoblotting using specific antibodies. The immunoreactive band intensities were analyzed by densitometry using ImageJ software and expressed in arbitrary units as a ratio of levels of phosphorylated protein to those of the total protein to correct for variation in the amount of protein. The relative levels of phosphorylated protein were also normalized to stimulated controls (value = 100%). Statistically significant differences were calculated by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s test (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 versus stimulated controls). Data are representative of three or more independent experiments.