Figure 6.
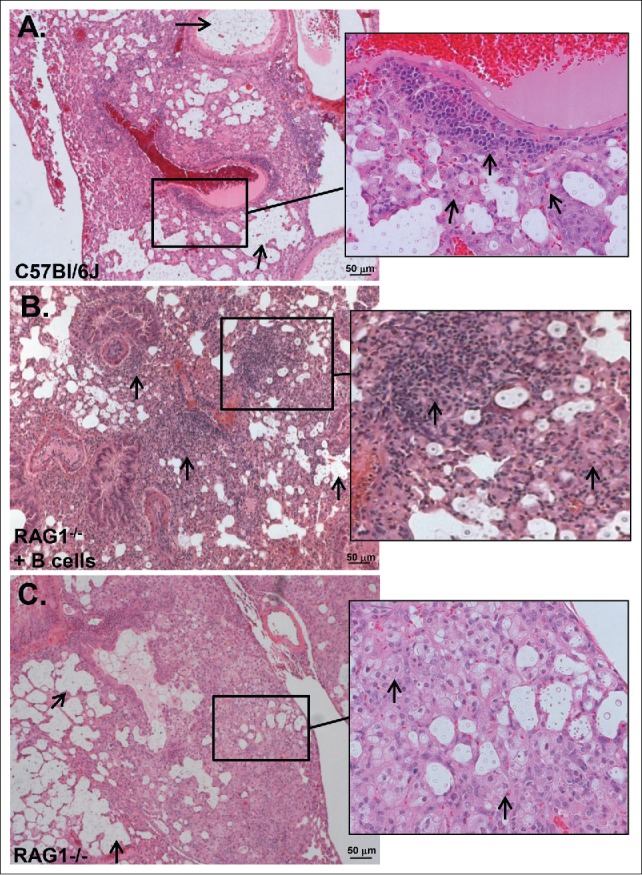
Inflammatory patterns (H&E) of C. neoformans-infected C57Bl/6 (wild-type), Rag1−/− mice that received (B)cells and Rag1−/− mice, 14 d post-infection. A) Wild-type mice. Arrows point to large collections of extracelluar organisms in airspaces. Inset: Organized granulomatous inflammation composed of polymorphonuclear leukocytes, lymphocytes, epithelioid cells and macrophages. Inset: arrows point to lymphocytes and macrophages associated with perivascular inflammation. Five mice were examined. (B) Rag1−/− mice that received peritoneal B cells. Arrows point to organized granulomatous inflammation composed of lymphocytes, polymorphonuclear leukocytes and macrophages associated with perivascular inflammation. There are also large collections of organisms in airspaces. Inset: arrows pointing to lymphocytes and macrophages in cellular infiltrate. Two mice were examined. (C) Rag1−/− mice. Arrows point to large collections of extracellular organisms in airspaces. Inset: Inflammatory cells are polymorphonuclear leukocytes, epitheloid cells and macrophages as shown by arrows. Five mice were examined. Scale bar = 50 um.
