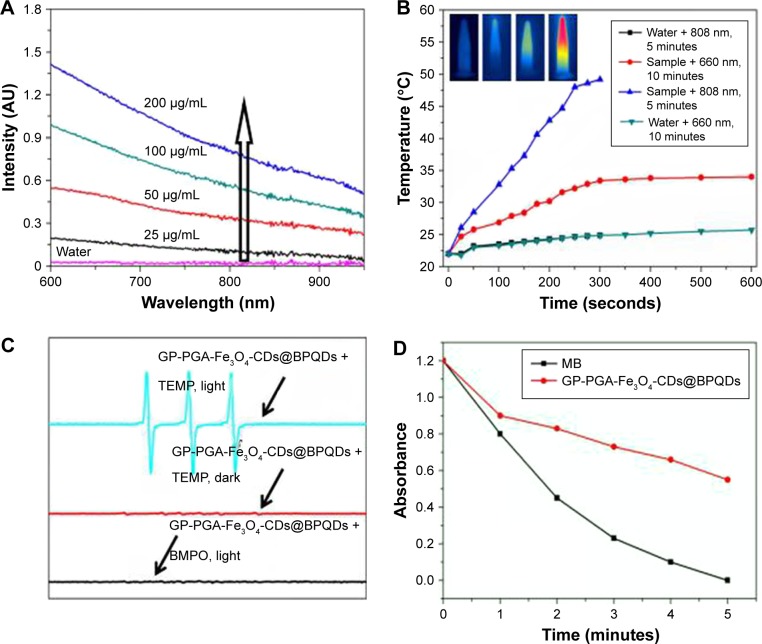
Figure 3.
Photochemical and photodynamic properties of GP-PGA-Fe3O4-CDs@BPQDs nanoplatform.
Notes: (A) Ultraviolet-visible NIR-absorption spectra of GP-PGA-Fe3O4-CD@BPQD nanoparticle solutions at different concentrations. The arrow represents the increasing concentration of the sample. (B) Temperature elevation of GP-PGA-Fe3O4-CD@BPQD nanoparticles (50 μg/mL) under irradiation with a 660 nm (0.5 W/cm2) or 808 nm (2 W/cm2) laser as a function of irradiation time. Inset, temperature IR images of an aqueous solution of GP-PGA-Fe3O4-CDs@BPQDs under 660 nm (0.5 W/cm2) or 808 nm (2 W/cm2) laser irradiation, which was recorded using an IR camera. (C) ESR spectra of GP-PGA-Fe3O4-CDs@BPQDs in the presence of TEMP in different conditions. Both the decomposition of DPBF and ESR spectra were carried out under an Xe lamp with a 600 nm cutoff filter. (D) Decay curves of Na2-ADPA absorption at 378 nm as a function of time in the presence of GP-PGA-Fe3O4-CDs@BPQDs and MB <660 nm laser irradiation (0.5 W/cm2). The arrows in part C represent the curve of the sample.
Abbreviations: NIR, near-infrared; GP, genipin; PGA, polyglutamic acid; CD, carbon dot; BPQD, black phosphorus quantum dot; ESR, electron-spin resonance; TEMP, 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine; DPBF, diphenylisobenzofuran; ADPA, anthracene-9,10-dipropionic acid; MB, methylene blue; BMPO, 5-tert-butoxycarbonyl-5-methyl-1-pyrroline-N-oxide.