Fig. 3. Telomeric and subtelomeric regions are lost in stn1-226 at a high temperature.
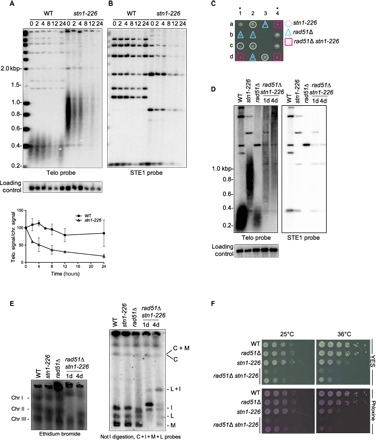
(A and B) WT and stn1-226 strains were cultivated at 25°C in YES medium and then shifted at 36°C for 24 hours. Genomic DNA was prepared, digested with Apa I restriction enzyme, and analyzed by Southern blotting with radiolabeled probes, telomeric probe (A), subtelomeric STE1 probe (B), and a chromosomic probe (used as a loading control). Quantification of normalized telomeric signal over chromosomic signal is shown in the lower panel. Error bars indicate the average from two independent experiments. At a restrictive temperature, both telomeric and subtelomeric signals disappeared in stn1-226. (C) Synthetic sickness of rad51Δ and stn1-226 alleles. Spore colonies, resulting from tetrad dissection of a mating between rad51Δ and stn1-226 mutants, were grown at 25°C. (D) Telomere length analysis of indicated strains grown at 25°C. Genomic DNA was prepared, digested with Apa I restriction enzyme, and analyzed by Southern blotting with radiolabeled telomeric, subtelomeric (STE1), and chromosomic probes (loading control). At a permissive temperature, the telomeric and subtelomeric signal disappeared in both rad51Δ stn1-226 double mutants. (E) Left: PFGE stained by ethidium bromide of intact chromosomes from WT strain, stn1-226, rad51Δ, and stn1-226 rad51Δ mutants grown at 25°C. Chromosomes I, II, and III entered into the gel. Right: Not I–digested genomic DNA was subjected to PFGE, transferred to nitrocellulose membrane, and hybridized with probes of telomere proximal fragments C, I, M, and L. The rad51Δ stn1-226 4D clone exhibited a partial circularization of its chromosomes, whereas clone 1D displayed a rearranged profile with partial circularization. (F) Analysis of viability of the indicated strains at 25° and 36°C. Cells were grown at 25°C, then serially diluted, and plated on YES-rich medium either complemented or not with phloxine.
