Fig. 5. Genetic interactions of stn1-226 allele with rpa1-D223Y, taz1Δ, rif1Δ, rif1-PP1, and rap1Δ.
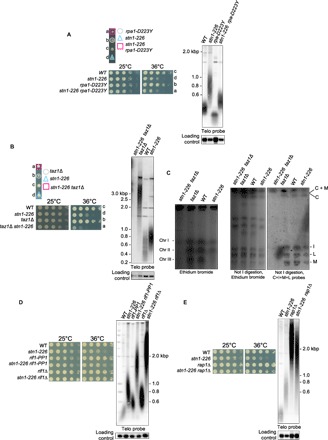
(A to E) Tetrad dissections, telomere length analysis, and viability of the indicated spore colonies are shown. Analysis of viability was carried out at 25° and 36°C. Cells were grown at 25°C, then serially diluted (fivefold), and plated on YES-rich medium. Cells were grown at 25°C, and genomic DNA was digested with Apa I restriction enzyme for telomere Southern blotting analysis. Loading control corresponds to a 2.4-kbp fragment of a chromosomic region. (C) Left: PFGE stained by ethidium bromide of intact chromosomes from WT strain, parental taz1Δ and stn1-226 single mutants, and taz1Δ stn1-226 double mutants. Chromosomes I, II, and III were stable in single mutants, whereas they did not enter into the gel in double mutants. Right: Not I–digested genomic DNA was subjected to PFGE, transferred to nitrocellulose membrane, and hybridized with probes of telomere proximal fragments C, I, M, and L. In taz1Δ stn1-226 double mutant, these fragments were absent, suggesting that chromosomes are circular.
