Fig. 3.
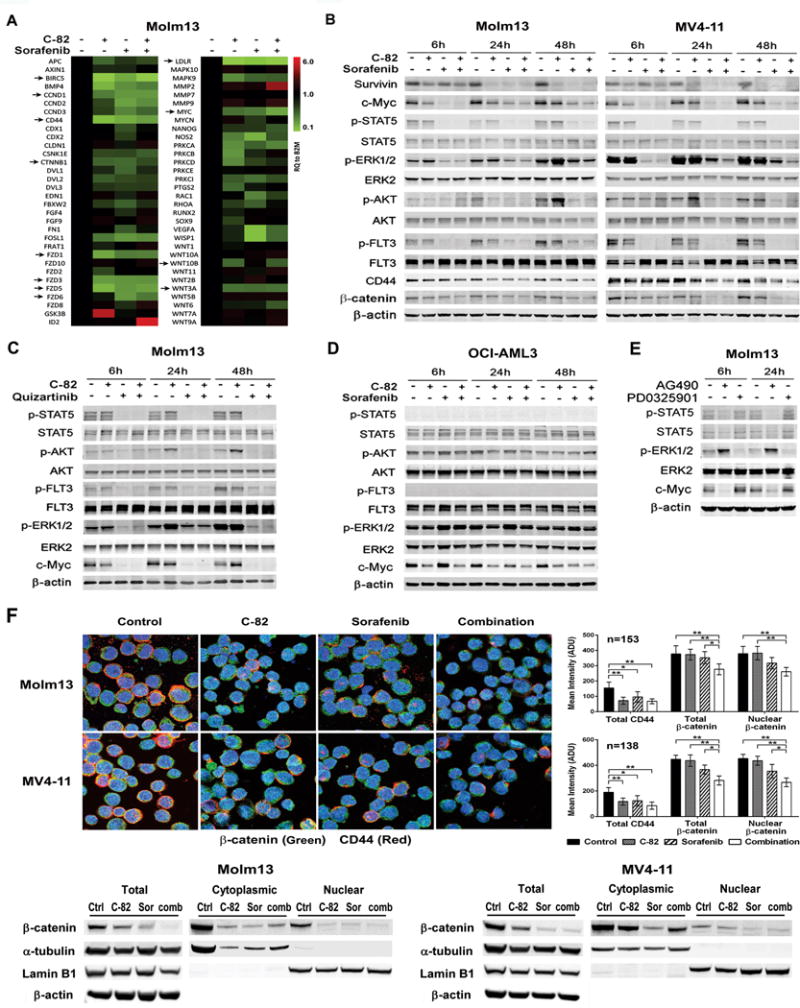
C-82 and TKI combination inhibits β-catenin/CBP and FLT3 signaling and reduces β-catenin nuclear localization in AML cells. (A) Molm13 cells were treated with C-82 (0.5 μM), sorafenib (20 nM), or both for 48 h, and RNA levels were determined by the Wnt signaling pathway PCR array (arrows indicate genes discussed in the text). (B) Expression of β-catenin/CBP and FLT3 signaling and downstream targets were analyzed by western blotting in Molm13 and MV4-11 cells treated with C-82 and sorafenib for 6, 24, 48 h. C-82 and sorafenib were 0.5 μM and 20 nM for Molm13 and 0.56 μM and 75 nM for MV4-11, respectively. (C) Molm13 cells were treated with C-82 (0.5 μM) and quizartinib (1.6 nM) and (D) OCI-AML3 cells were treated with C-82 (0.5 μM) and sorafenib (20 nM) for 6, 24, and 48 h. (E) Molm13 cells were treated with JAK/STAT inhibitor AG490 (100 μM) or MEK/ERK inhibitor PD0325901 (200 nM) for 6, 24 h. Protein expressions were determined by western blot analysis. (F) Confocal image (1000×) and quantifications illustrating expressions of β-catenin and CD44, and the nuclear localization of β-catenin (top) and β-catenin levels in total, cytoplasmic, and nuclear fractions by western blot analysis (bottom) in Molm13 or MV4-11 cells treated with C-82 (0.5 or 0.56 μM), sorafenib (20 or 75 nM), or both for 48 h. Ctrl, control; Sor, sorafenib; Comb, combination. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01.
