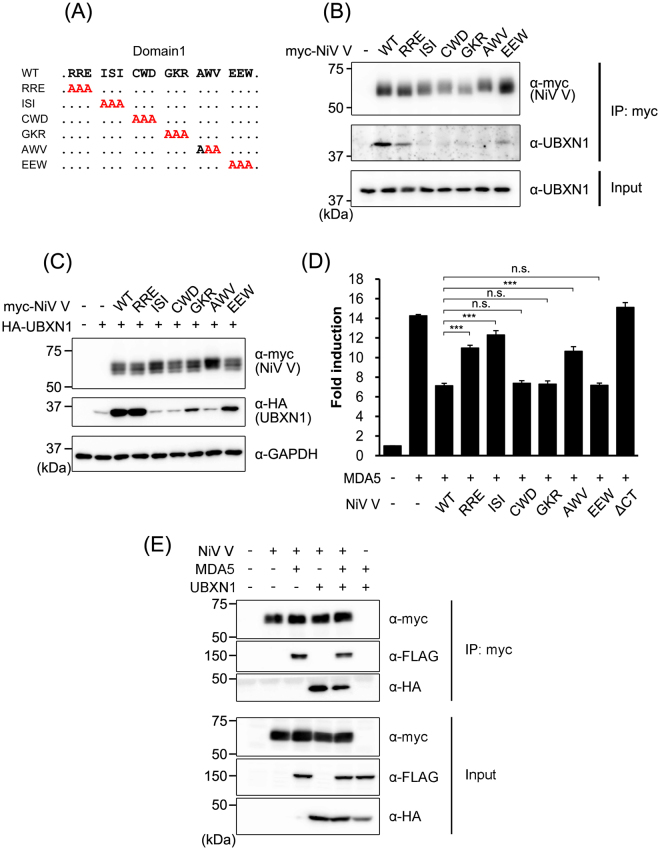
Figure 5.
Amino acids in NiV V required for its interaction with UBXN1. (A) Schematic diagrams of the alanine-substitution mutants of NiV V are shown. (B) Myc-tagged wild-type NiV V and its alanine-substitution mutants were expressed in HEK293T cells, and an immunoprecipitation assay and western blotting were performed as described in Fig. 1B. (C) HEK293T cells were transfected with equal amounts of vector expressing HA-tagged UBXN1 and vector expressing myc-tagged wild-type NiV V or its alanine-substitution mutants. At 48 h posttransfection, the proteins were detected with western blotting. (D) HEK293T cells were transfected with an IFNβ reporter vector together with vectors expressing FLAG-tagged MDA5 and wild-type NiV V or its alanine-substitution mutants. The total amount of transfected vector was kept constant by the addition of empty vector. At 24 h posttransfection, a luciferase assay was performed. (E) HEK293T cells were transfected with vectors expressing myc-tagged NiV V, FLAG-tagged MDA5 and HA-tagged UBXN1. At the 48 h posttransfection, an immunoprecipitation assay was performed with anti-myc antibody. The precipitated proteins were detected with western blotting. Error bars indicate standard deviations (N = 3). ***P < 0.001, not significant (n.s.) on Dunnett’s multiple comparison test. The blots presented in (B,C,E) were cropped from different images to improve clarity. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Figure S4.