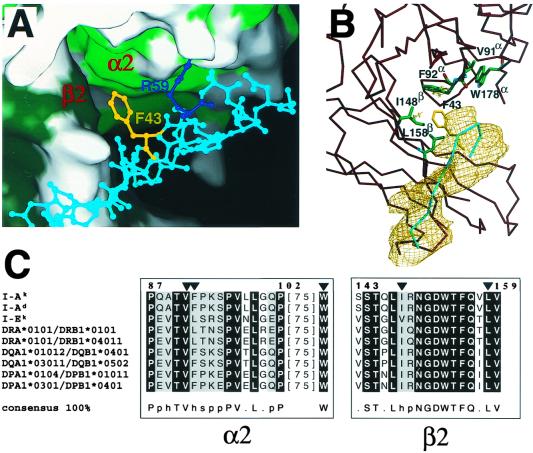
Figure 2.
The conserved hydrophobic pocket formed by class II MHC α2 and β2 domain residues into which CD4 Phe-43 inserts. (A) Class II MHC is depicted in surface representation form and adjacent CD4 residues in ball-and-stick format. Hydrophobic residues from domain α2 (light green) and domain β2 (dark green) of the I-Ak molecule are shown. The positions of the side chains of Phe-43 (yellow) and Arg-59 (blue) have been optimized by molecular dynamics by using cns (24). The surface representation was prepared with spock. (B) The same region is presented with residues that contribute to the hydrophobic pocket shown, including Val-91, Phe-92, and Trp-178 from the α2 domain and Ile-148 and Leu-158 from the β2 domain of the MHC class II molecule in green. The Cα trace of the MHC class II molecule in this region is depicted in dark red. The Cα trace of the C" strand of the CD4 molecule is depicted in cyan, and the Phe-43 residue is shown in yellow. A portion of an omit map at a contour level of 1σ is shown in gold for the C" strand of CD4, which was obtained by rigid body refinement with this segment excluded from the calculation. (C) Sequence alignment of the highly conserved contact regions in MHC class II for different murine (I-Ak, I-Ad, and I-Ek) and human (DRA*0101/DRB1*0101, DRA*0101/DRB1*04011, DQA1*01012/DQB1*0401, DQA1*03011/DQB1*0502, DPA1*0104/DPB1*01011, DPA1*0301/DPB1*0401) alleles by using clustalx (48). Residues Val-91, Phe-92, and Trp-178 of the α2 domain and Ile-148 and Leu-158 of the β2 domain are indicated by a triangle. The consensus is defined so that entirely conserved residues are depicted by their amino acid code, whereas p indicates conservation of a polar residue, h conservation of a hydrophobic residue, and s conservation of a small side-chain-containing residue.