Fig. 1.
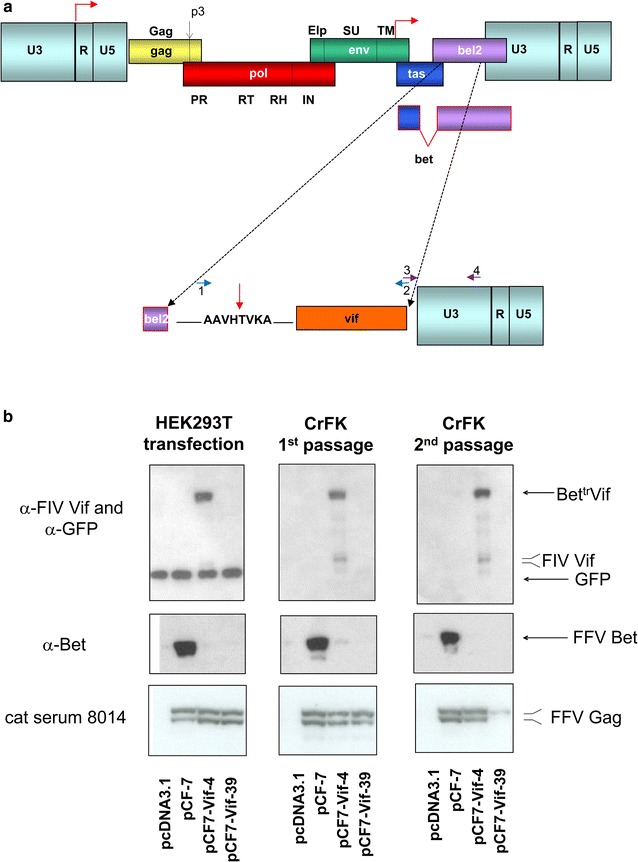
Schematic presentation of the construction of FFV-Vif chimeras and their molecular features. a Schematic presentation of the FFV genome with its genes and protein domains as well as the LTR and internal promoters (red bent arrows, top) and presentation of the engineered BettrVif fusion protein (bottom). The non-functional N-terminus of bet (purple) was fused in-frame to the codon-optimized FIV vif gene including the vif ATG start codon. A short linker encompassing the FFV PR cleavage site (vertical red arrow, bottom) was inserted between the N-terminus of Bet and Vif. Primer pairs used to insert the vif gene into the FFV genome are shown in blue and violet and with numbering in the bottom panel. b HEK 293T cells were transfected with wild-type pCF-7, functional clone pCF7-Vif-4, non-functional clone pCF7-Vif-39, and pcDNA3.1 control DNA. Two days after transfection, cell culture supernatants and cells were harvested as described in the “Methods” section. Cleared supernatants were used for serial passaging in feA3-expressing CrFK cells and FFV titer determination (Fig. 2a). At 3 days p.i., infected CrFK cells and supernatants were harvested and used as above. Cell lysates from transfected HEK 293T cells and CrFK cells after the first and second passage were subjected to immunoblotting against FIV Vif and co-transfected GFP, FFV Bet, and FFV Gag (cat serum 8014). The positions and names of the detected proteins are given at the right margin
