Fig. 2.
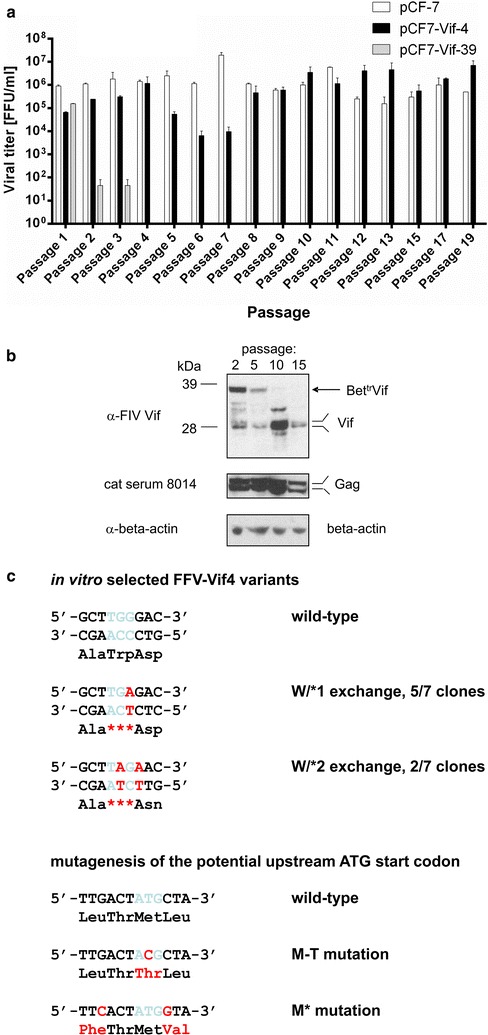
In vitro selection and molecular characterization of pCF7-Vif-4 variants with increased replication competence. Plasmids pCF7-Vif-4, -39, and pCF-7 were transfected into HEK 293T cells. Two days after transfection, cell-free supernatants were inoculated on CrFK cells and serially passaged twice a week on CrFK cells (every 3 or 4 days) as described above for Fig. 1b. a FFV titers were determined in duplicate using FeFAB reporter cells and are shown as bar diagram for selected passages over time. Error bars represent the standard deviation. b Selected cell extracts from the CrFK passages were subjected to immunoblotting. The immune-detection with a Vif-specific antiserum initially showed mainly the engineered BettrVif and the proteolytically released Vif, then various unidentified Vif variants, and finally (passages 10 and 15) predominantly the authentic Vif protein. FFV Gag proteins were detected in all samples as expected using cat antiserum 8014 while in the bottom panel the β-actin loading control is shown. c Sequence context of the in vitro-selected W/* mutations (light blue original Trp to the stop codon in red) suggests feA3 editing of the minus strand of FF7-Vif-4-derived reverse transcription intermediates in the PyPyC sequence context (top panel, Py = pyrimidine residue). Below, mutagenesis of the in-frame ATG 14 codons upstream of the vif gene is shown only for the sense strand (bottom panel). The ATG start codon is shown in light blue and the engineered residues and changes amino acids are in red
