Fig. 8.
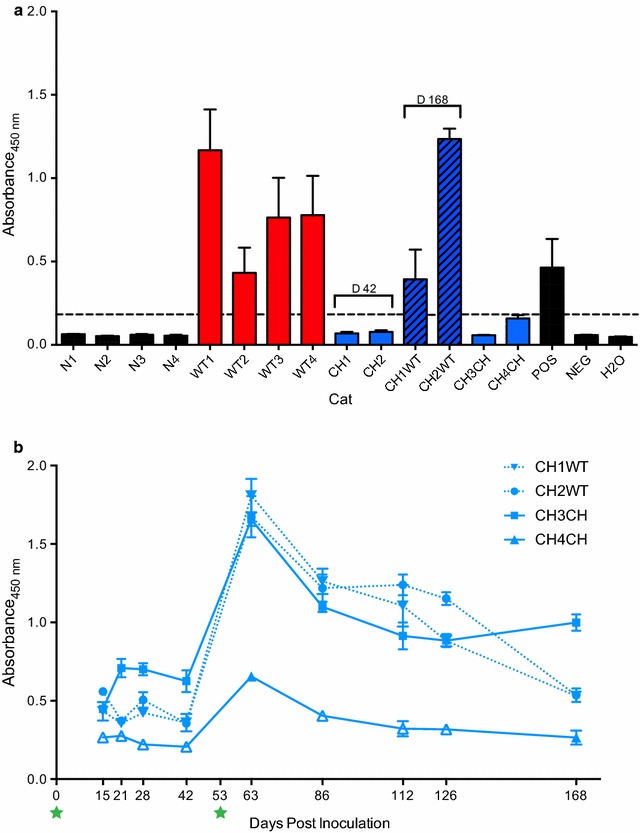
Animals inoculated with wild-type FFV or FFV-Vif chimera seroconverted to FFV Bet or FIV Vif. Antibody response against FFV Bet and FIV Vif antigens were measured by antibody capture ELISAs as described in the “Methods” section. a Anti-Bet antigen reactivity for each animal at final time points unless specified. WT cats (red bars), and cats that received chimera and then wild-type FFV (CH×WT, black and blue striped bars) seroconverted against Bet. Animals exposed to only FFV-Vif W/*1 (cats CH1 and CH2 prior to day 53, and CH3CH and CH4CH, solid blue bars) were negative for anti-Bet antibodies as expected. Black bars show naïve cats, and positive and negative control samples. b Three out of 4 animals inoculated with chimeric virus developed a detectable anti-Vif immune response as early as 15 days p.i. Antibody response increased following re-inoculation for all animals, causing a detectable response in the fourth animal (CH4CH), though sero-reactivity was low compared to other animals for this individual, and only rose above positive cutoff absorbance on days 63 and 168. Filled shapes indicate positive ELISA absorbance values compared to negative controls (> 2 standard deviation above the mean of duplicate negative samples), whereas open triangles for CH4CH indicate ELISA absorbance values below positive cutoff. Values reported represent mean of duplicate samples and bars indicate standard deviation
