Fig. 1.
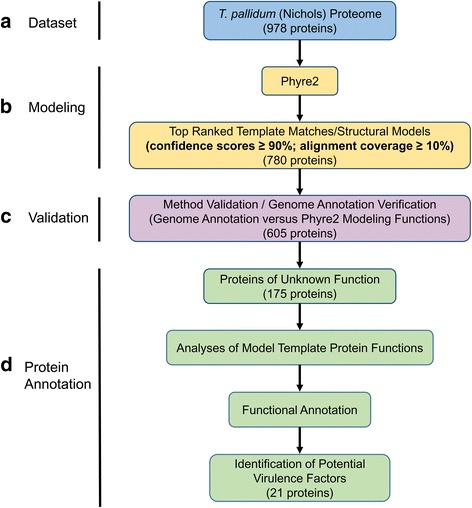
Pipeline for proteome-wide tertiary structure modeling of T. pallidum. a Dataset: All 978 proteins from T. pallidum subspecies pallidum (Nichols) were used for whole proteome tertiary structure modeling and functional predictions. b Modeling: Complete amino acids sequences corresponding to the 978 protein-coding genes were submitted in “batch-mode” to the protein tertiary structure modeling server, Phyre2, and the 20 top-ranked template structural matches for each protein were obtained. Only those T. pallidum proteins that were modeled with a Phyre2 confidence score of at least 90% and alignment coverage of at least 10% were analyzed further. c Validation: To help validate our approach and increase confidence in previous genomic annotations, the predicted functions (based on tertiary structure model template information) of 605 T. pallidum proteins were compared with their corresponding functional annotations derived from genome sequencing. Proteins were then categorized as having either the same, related, or different functions. d To gain insight into the potential function(s) of 175 uncharacterized proteins, and for the identification of potential virulence factors, the functions of the 20 top-ranked tertiary structure model templates for each protein were analyzed using the same confidence and alignment coverage cut-off scores as described above
