Table 1.
Adiponectin-Secreting Activity of 1a and Related A3 AR Ligandsa
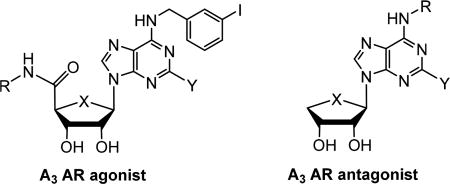
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||||
| adiponectin (pg/mL)c | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||
| compd | X | Y | R |
Ki (hA1AR) (nM)b or % displacement at 1 µM |
Ki (hA2AAR) (nM)b or % displacement at 1 µM |
Ki (hA3AR) (nM)b or % displacement at 1 µM |
20 µM | 4 µM |
| A3 AR agonists | ||||||||
| 1a | O | H | CH3 | 51.2 ± 5.1 | 2910 ± 580 | 1.8 ± 0.7 | 216 ± 12** | 117 ± 20 |
| 1b | O | Cl | CH3 | 222 ± 22 | 5360 ± 2470 | 1.4 ± 0.3 | 603 ± 10** | 221 ± 10** |
| 1c | S | H | CH3 | 20.2 ± 2.9 | 475 ± 144 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 343 ± 20** | 126 ± 14 |
| 1d | S | Cl | CH3 | 193 ± 46 | 223 ± 36 | 0.38 ± 0.07 | 738 ± 59** | 131 ± 10 |
| 2a | S | H | CH2CH3 | 5.4 ± 0.3 | 57.6 ± 6.9 | 0.42 ± 0.22 | 242 ± 4** | 118 ± 38 |
| 2b | S | H | cyclopropyl | 9.27 ± 0.83 | 15.2 ± 2.6 | 3.03 ± 0.23 | 249 ± 26** | 174 ± 5** |
| 2c | S | H | cyclopropyl-CH2 | 159 ± 40 | 1600 ± 80 | 2.16 ± 0.29 | 490 ± 16** | 242 ± 11** |
| 2d | S | H | cyclobutyl | 23.6 ± 4.2 | 122 ± 62 | 1.17 ± 0.16 | 633 ± 39** | 323 ± 30** |
| A3 AR antagonists | ||||||||
| 3a | S | Cl | 3-I-Bn | 2490 ± 940 | 341 ± 75 | 4.16 ± 0.5 | 857 ± 69** | 192 ± 19* |
| 3b | S | Cl | 3-Cl-Bn | 38% | 18% | 1.66 ± 0.9 | 442 ± 5** | 196 ± 1** |
| 3c | S | Cl | 2-Cl-Bn | 13% | 1600 ± 135 | 25.8 ± 6.3 | 268 ± 14** | 107 ± 6 |
| 3d | S | H | 3-Cl-Bn | 860 ± 210 | 440 ± 110 | 1.5 ± 0.4 | 247 ± 7** | 163 ± 12* |
| IDX control | 100 ± 6 | |||||||
| glibenclamide | 1000 ± 193** | 838 ± 67** | ||||||
Results are the mean ± SD of three measurements using hBM-MSCs from three independent donors (n = 3, three independent experiments):
p ≤ 0.05 and
p ≤ 0.01.
Binding affinities of 1a and related A3 AR ligands to human A1, A2A, and A3 AR were previously reported.27,29
In the IDX medium, 1a and related A3 AR ligands were included to induce adipogenesis in hBM-MSCs. On the 7th day in culture, cell culture supernatants were harvested and ELISA was performed to measure levels of adiponectin.
