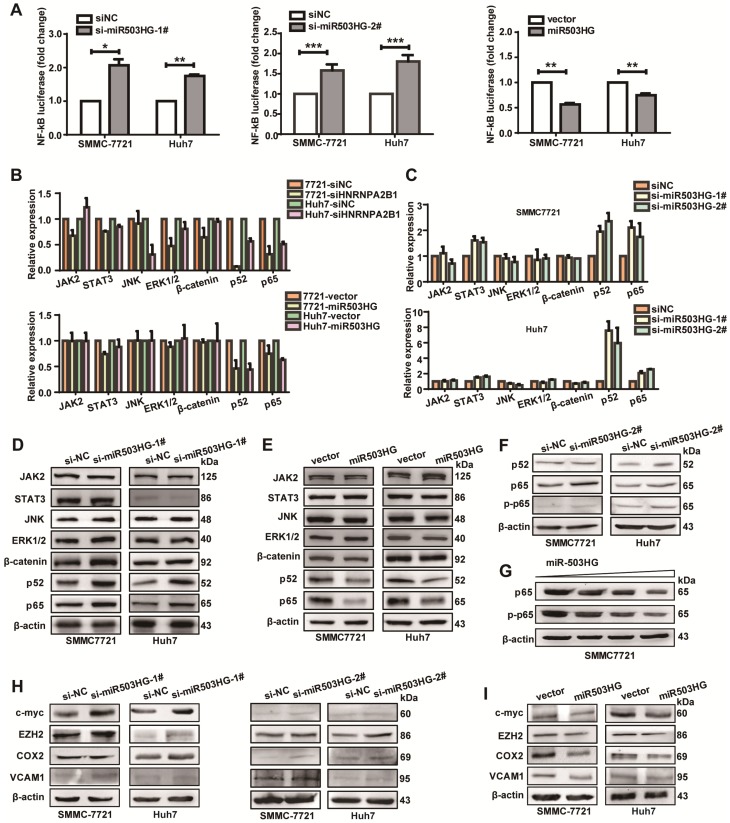
Figure 5.
miR503HG inhibits the NF-κB signaling pathway in HCC cells. (A) Relative luciferase activity of NF-κB in miR503HG-downregulated or -upregulated SMMC-7721 and Huh7 cells. The values are presented as the mean ± standard error of the ratio of firefly luciferase activity to Renilla luciferase activity and are representative of three independent experiments. Data are the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001. (B) Real-time PCR analysis of the expression of JAK2, STAT3, JNK, ERK1/2, β-catenin, p52 and p65 in HNRNPA2B1 silenced (top) and miR503HG-overexpressing HCC cells (bottom). (C) The mRNA levels of JAK2, STAT3, JNK, ERK1/2, β-catenin, p52, and p65 in HCC cells with miR503HG knockdown. (D-E) Western blotting analysis shows changes in JAK2, STAT3, JNK, ERK1/2, β-catenin, p52, and p65 in miR503HG-downregulated and miR503HG-upregulated HCC cells. β-actin was used as the loading control. (F) Knockdown of miR503HG could increase the phosphorylation levels of p65 in HCC cells. (G) Overexpression of miR503HG decreased endogenous p65 and phospho-p65 in a dose-dependent manner. (H-I) The protein levels of the NF-κB downstream effectors were determined by western blotting analyses in miR503HG-downregulated or -upregulated HCC cells.