Figure 7. Hyde1 proteins of Acidovorax citrulli AAC00-1 are toxic to E. coli and various PA bacterial strains.
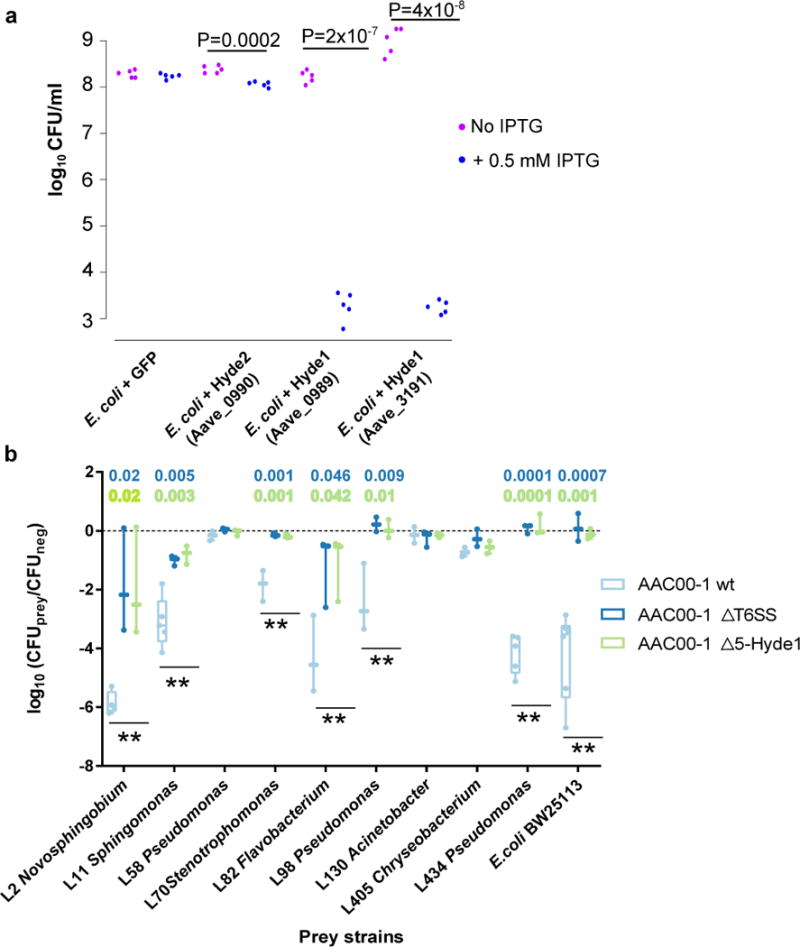
a. Toxicity assay of Hyde proteins expressed in E. coli. GFP, Hyde2 - Aave_0990, and two Hyde1 genes from two loci, Aave_0989 and Aave_3191, were cloned into pET28b and transformed into E. coli C41 cells. Aave_0989 and Aave_3191 proteins are 53% identical. Bacterial cultures from five independent colonies were spotted on LB plate. Gene expression of the cloned genes was induced using 0.5 mM IPTG. P values indicate significant results (two sided t-test). b. Quantification of recovered prey cells after co-incubation with Acidovorax aggressor strains. Antibiotic-resistant prey strains E. coli BW25113 and nine different Arabidopsis leaf isolates were mixed at equal ratios with different aggressor strains or with NB medium (negative control). Δ5-Hyde1 contains deletion of five Hyde1 loci (including nine out of 11 Hyde1 genes). ΔT6SS contains a vasD (Aave_1470) deletion. After co-incubation for 19 hours on NB agar plates, mixed populations were resuspended in NB medium and spotted on selective antibiotic-containing NB agar. Box plots of at least three independent experiments with individual values superimposed as dots are shown. Double asterisks denote a significant difference (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD test) between wild type vs. ΔT6SS, and wild type vs. Δ5-Hyde1, with P values denoted on top. Full strain names and statistical information appear in Supplementary Table 25. For a time course experiment with exemplary strains see Supplementary Figure 29.
