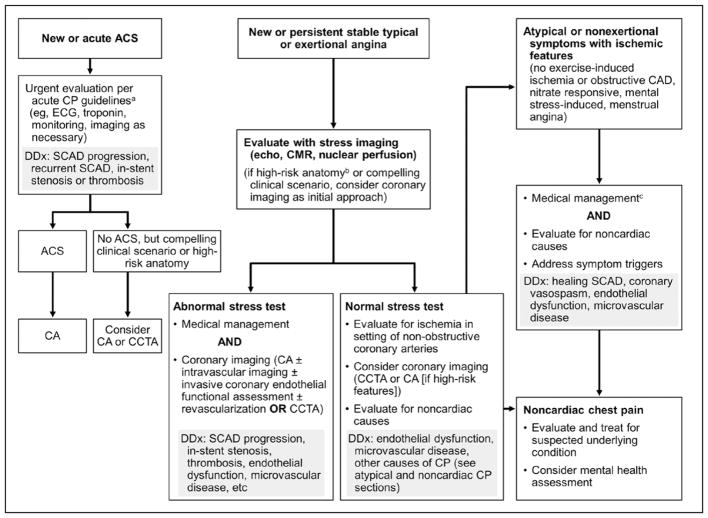
Figure 9. Evaluation and management of chest pain after spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD).157,170.
aCurrent guidelines.135 bHigh-risk anatomy indicates SCAD affecting the left main or 2 proximal coronary arteries. cMedical management for post-SCAD chest pain (CP) without obstructive disease: long-acting nitrates, calcium channel blockers, or ranolazine. ACS indicates acute coronary syndrome; CA, coronary angiography; CAD, coronary artery disease; CCTA, coronary computed tomography angiography; CMR, cardiac magnetic resonance; DDx, differential diagnosis; and echo, echocardiography.