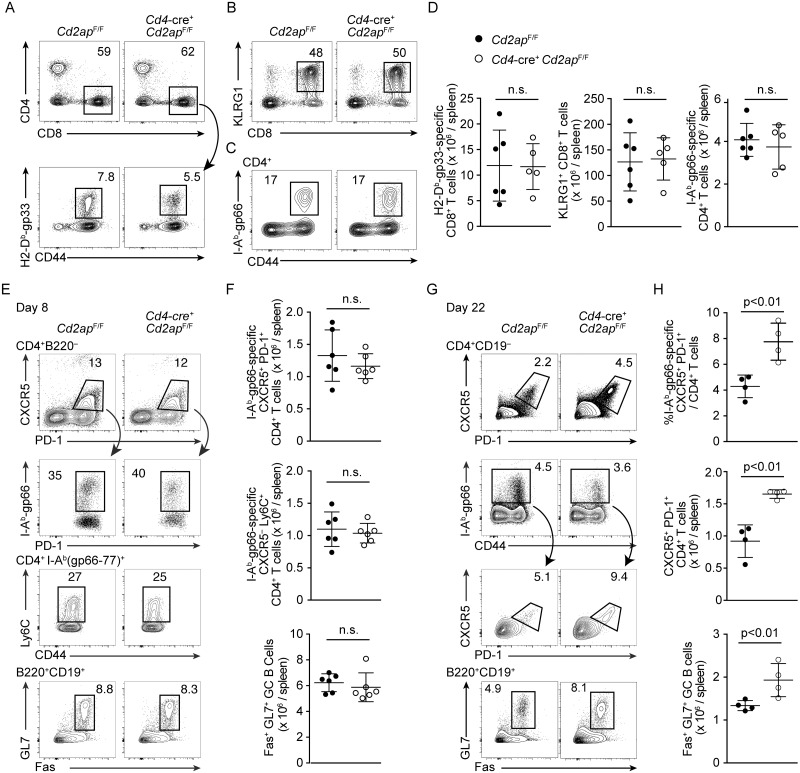
Fig 1. Enhanced TFH and GC B cell responses in T cell-specific Cd2ap-deficient mice in response to acute viral infection.
(A) Flow cytometric analysis of expression of CD4, CD8 and CD44 and binding of H-2Db(gp33-41) tetramer in splenocytes 8 days after LCMV-Armstrong infection. Total CD8 T cells and LCMV-gp33-specific CD8 T cells are shown with rectangular gates. (B) Expression of CD8 and KLRG1 in splenocytes 8 days after LCMV-Armstrong infection. (C) Expression of CD44 and binding of I-Ab(gp66-77) tetramer in CD4+ splenic T cells 8 days after LCMV-Armstrong infection. LCMV-gp66-specific CD4 T cells are shown with rectangular gates. (E, G) Expression of PD-1, CXCR5 and Ly6C and binding of I-Ab (gp66-77)+ tetramer of CD4+ T cells and Fas and GL7 expression in B cells in the spleens of Cd4-cre+ Cd2apF/F and control Cd2apF/F mice 8 (E) and 22 (G) days after infection. TFH cells and GC B cells are shown with rectangular gates. Representative plots are shown with percentages of gated cells. Statistical analyses from 4–6 mice in 2 independent experiments are shown with means and standard deviation in (D, F, H).